Abstract
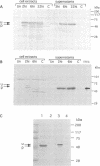
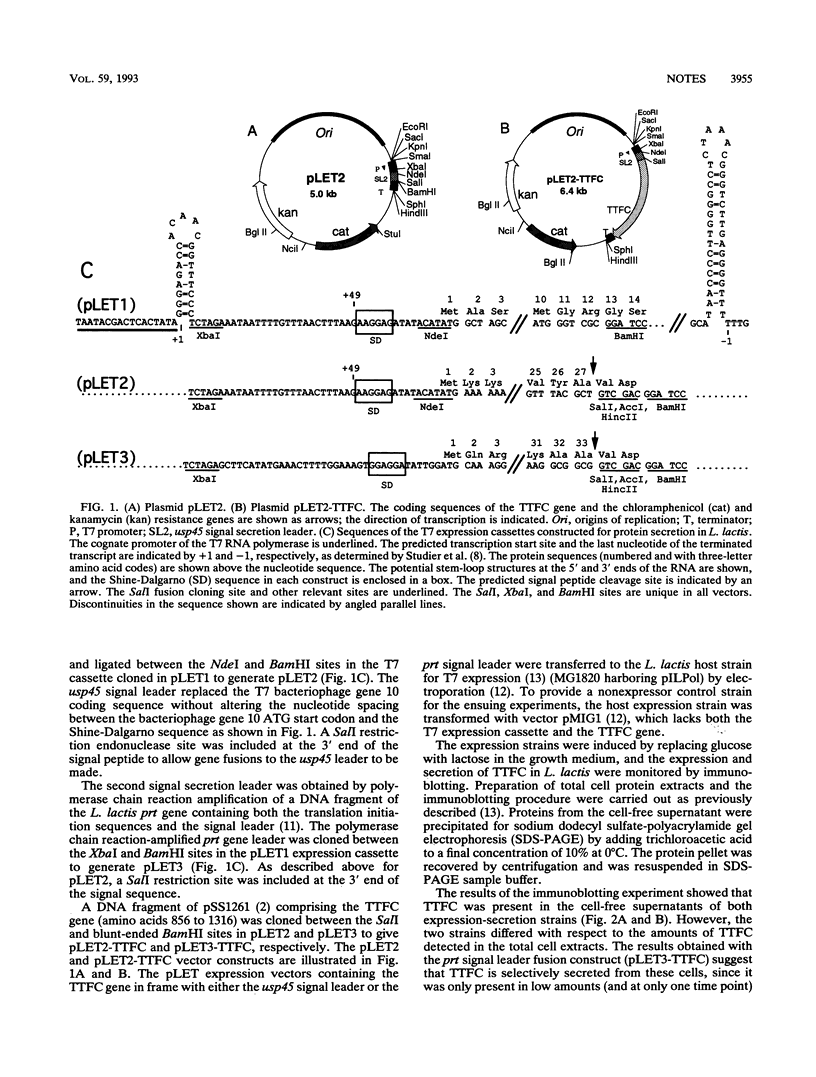
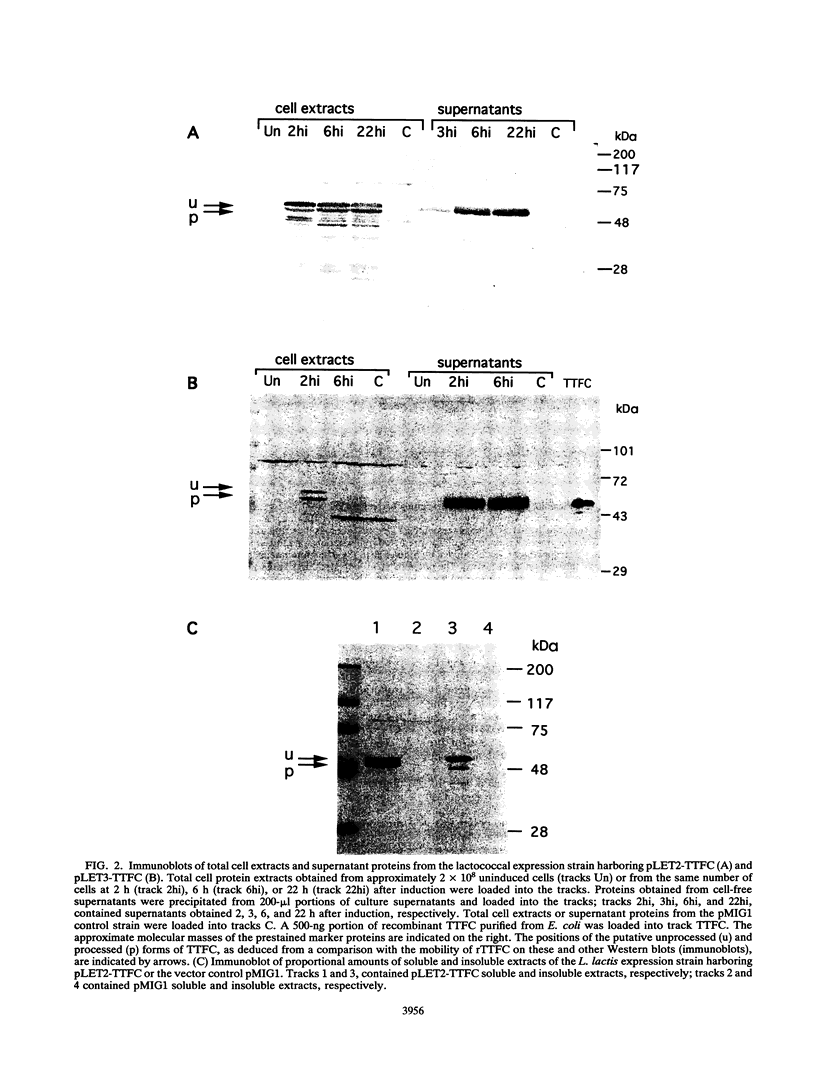
The capacity of recombinant strains of Lactococcus lactis to secrete a heterologous protein was investigated by constructing two expression-secretion vectors (pLET2 and pLET3) for use with a lactococcal gene expression system driven by the highly active T7 RNA polymerase. The vectors incorporated different lactococcal secretion leaders and translation initiation sequences. When tetanus toxin fragment C (TTFC) was used as a test protein, the quantities of TTFC produced by the pLET2-TTFC strain exceeded the rate of secretion of TTFC into the growth medium. However, nearly all of the soluble TTFC associated with the cell (3.4%) was translocated through the cell membrane. The pLET3-TTFC strain did not accumulate TTFC intracellularly and exhibited growth characteristics and viability identical to the growth characteristics and viability of the control strain. This strain secreted approximately 2.9 mg of TTFC per liter into the growth medium after 6 h of growth under test tube conditions. Our results indicate that L. lactis is capable of secreting substantial amounts of heterologous protein and also confirm the findings of other workers that the cell wall may serve as a functional barrier to the diffusion of some secreted proteins into the growth medium.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Halpern J. L., Habig W. H., Neale E. A., Stibitz S. Cloning and expression of functional fragment C of tetanus toxin. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1004–1009. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1004-1009.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Martinez G., Kok J., Venema G., van Dijl J. M., Smith H., Bron S. Protein export elements from Lactococcus lactis. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Sep;234(3):401–411. doi: 10.1007/BF00538699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibakov M., Koivula T., von Wright A., Palva I. Secretion of TEM beta-lactamase with signal sequences isolated from the chromosome of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Feb;57(2):341–348. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.2.341-348.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon D., Chopin A. Construction of a vector plasmid family and its use for molecular cloning in Streptococcus lactis. Biochimie. 1988 Apr;70(4):559–566. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H., Bron S., Van Ee J., Venema G. Construction and use of signal sequence selection vectors in Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3321–3328. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3321-3328.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stader J. A., Silhavy T. J. Engineering Escherichia coli to secrete heterologous gene products. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:166–187. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85017-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos P., Simons G., Siezen R. J., de Vos W. M. Primary structure and organization of the gene for a procaryotic, cell envelope-located serine proteinase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13579–13585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. M., Wilson P. W., Le Page R. W. Improved cloning vectors and transformation procedure for Lactococcus lactis. J Appl Bacteriol. 1993 Jun;74(6):629–636. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1993.tb05195.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. M., Wilson P. W., Norton P. M., Gasson M. J., Le Page R. W. Lactococcus lactis: high-level expression of tetanus toxin fragment C and protection against lethal challenge. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jun;8(6):1155–1162. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Asseldonk M., Rutten G., Oteman M., Siezen R. J., de Vos W. M., Simons G. Cloning of usp45, a gene encoding a secreted protein from Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis MG1363. Gene. 1990 Oct 30;95(1):155–160. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90428-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Guchte M., Kodde J., van der Vossen J. M., Kok J., Venema G. Heterologous gene expression in Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis: synthesis, secretion, and processing of the Bacillus subtilis neutral protease. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Sep;56(9):2606–2611. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.9.2606-2611.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]