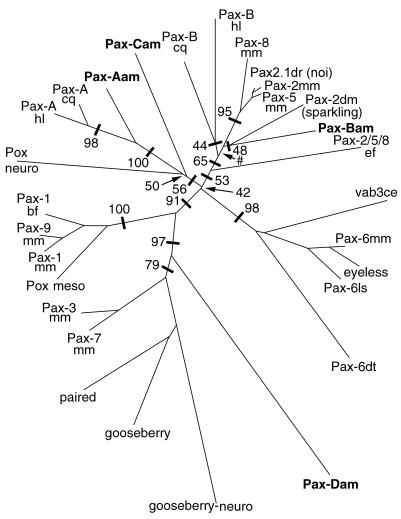
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic analysis of PD sequences. The tree is shown as an unrooted phylogram and is the result of distance analysis (neighbor-joining method) with paup4b2 (25); 127 rather than 128 amino acids have been used in the analysis, because that is all of the sequence available for Pax-Bcq. Numbers along branches indicate the percentage of 1,000 bootstrap replicates supporting the topology shown. For clarity, some bootstrap values are omitted. The symbol # indicates <40% bootstrap support. The analysis shown includes the sponge sequence sPax-2/5/8 (as Pax-2/5/8ef); note that when this divergent sequence was excluded, bootstrap support for the large clade comprising the cnidarian Pax-B and eumetazoan Pax-2/5/8 sequences increased significantly to 87%. For consistency and simplicity in labeling, Drosophila proteins have retained their original names, but other protein names containing a “Pax-X” in their name have been relabeled according to the formula (Pax) + (designation) + (abbreviation of genus and species). Thus, sPax-2/5/8 from the sponge Ephydatia fluviatilis (20) has been designated Pax-2/5/8ef in the figure.