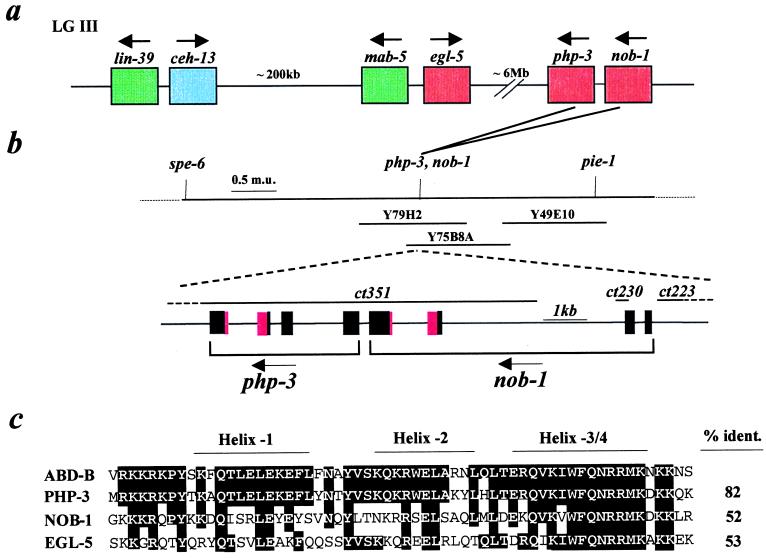
Figure 1.
Mapping, cloning, and sequence analysis of nob-1 and php-3 genes. (a) Arrangement of the C. elegans Hox genes. The anterior-group gene is indicated in blue; medial-group genes are indicated in green; and posterior-group genes are indicated in red. Arrows indicate directions of transcription. kb, kilobase; Mb, megabase. (b) Genomic organization and mutant lesions of nob-1 and php-3. Partial genetic and physical maps show location of nob-1 and php-3 on LGIIIR and on yeast artificial chromosomes Y79H2 and Y75B8A. The extent of each deletion mutation is shown above the genes. Dots extending toward the right and left under ct223 and ct351, respectively, indicate that these deletions extend beyond the boundaries of the figure (see text). m.u., map units (centimorgans). (c) Sequence alignment of predicted homeodomains encoded by Drosophila AbdB and C. elegans posterior-group genes php-3, nob-1, and egl-5. Shading indicates identities between AbdB and the C. elegans sequences. The percentage of identity (% ident.) between AbdB and each of the C. elegans genes is shown at the right.