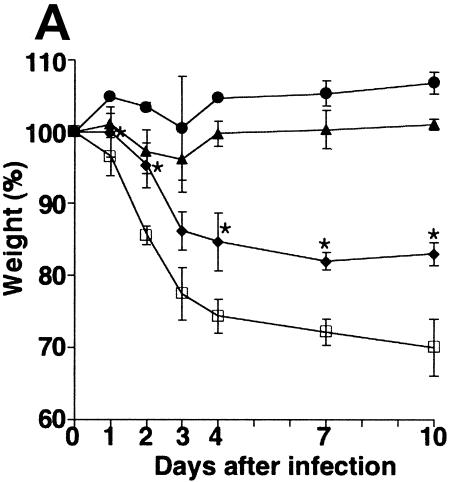
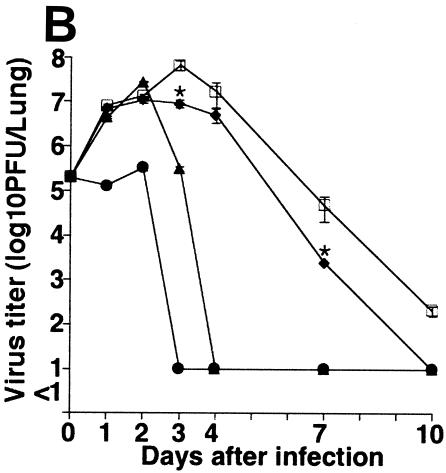
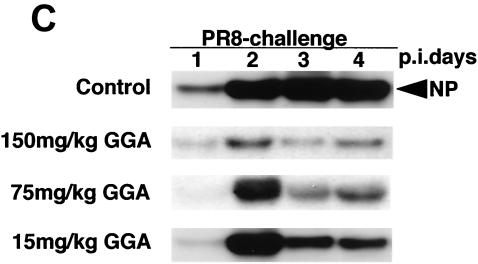
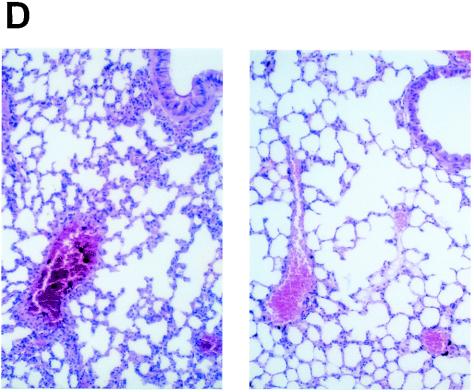
FIG. 1.
Effect of GGA administration on strain PR8-infected mice. (A) Effect of GGA on weight loss. Mice were divided into four groups with vehicle or GGA administered as follows: (i) vehicle (control group) (open squares; n = 30); (ii) 150 mg of GGA/kg of body weight (closed circles; n = 30); (iii) 75 mg of GGA/kg (closed triangles; n = 30); and (iv) 15 mg of GGA/kg (closed diamonds; n = 30). We then inoculated these mice intranasally with influenza A virus (A/PR8/34 [H1N1]) and monitored them for 10 days. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM of the results for one group (Fisher's PLSD; *, P < 0.05 versus control). (B) Viral titers in mouse lung tissue determined with a plaque assay. Titers were determined via serial dilutions of lung homogenates onto MDCK monolayer cells for detection of PFU. The results are a combination of those obtained in three separate experiments. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM of the results for one group (Fisher's PLSD; *, P < 0.01 versus control). (C) Western blot analysis of viral NP synthesis in lung tissues at an early stage. (D) Histopathologic features of the lungs of PR8-infected mice treated with or without GGA at 10 days p.i. Left panel, results for vehicle-treated control; right panel, results from treatment with 150 mg of GGA/kg. (Hematoxylin and eosin staining was used; original magnification, ×200.)