Fig. 1.
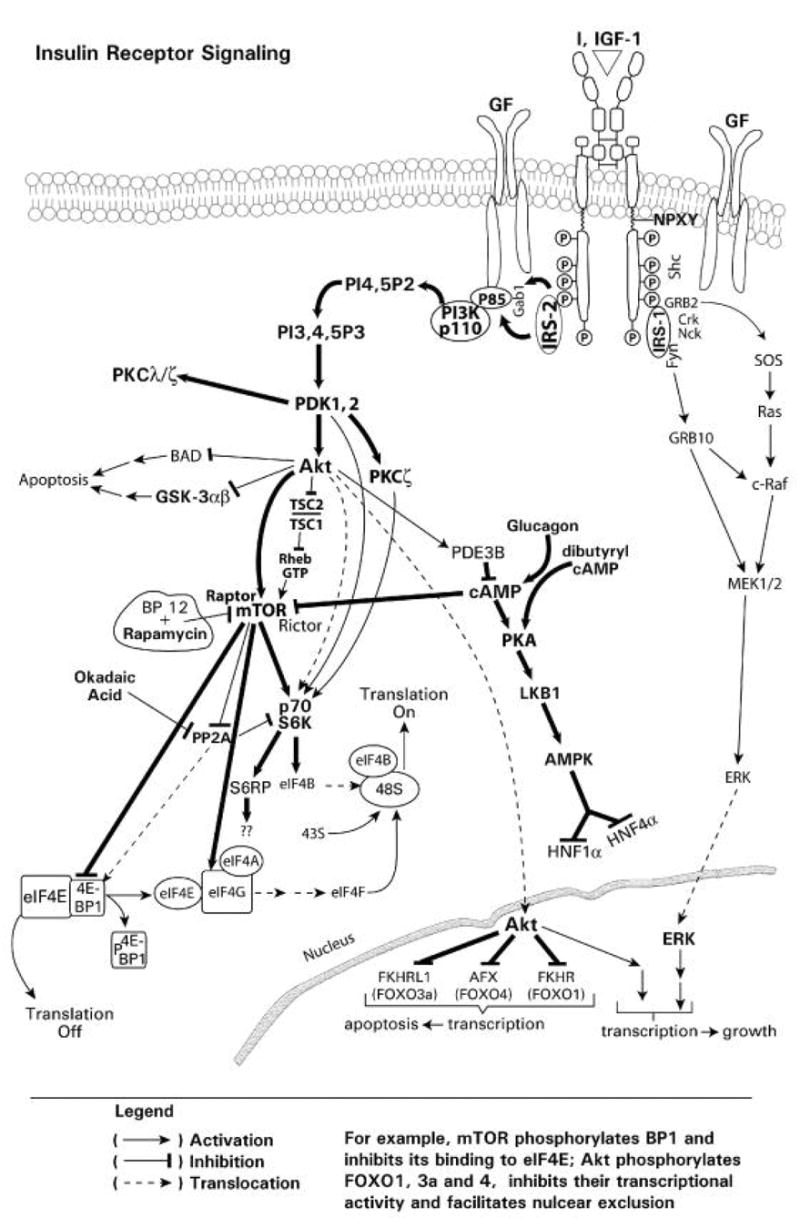
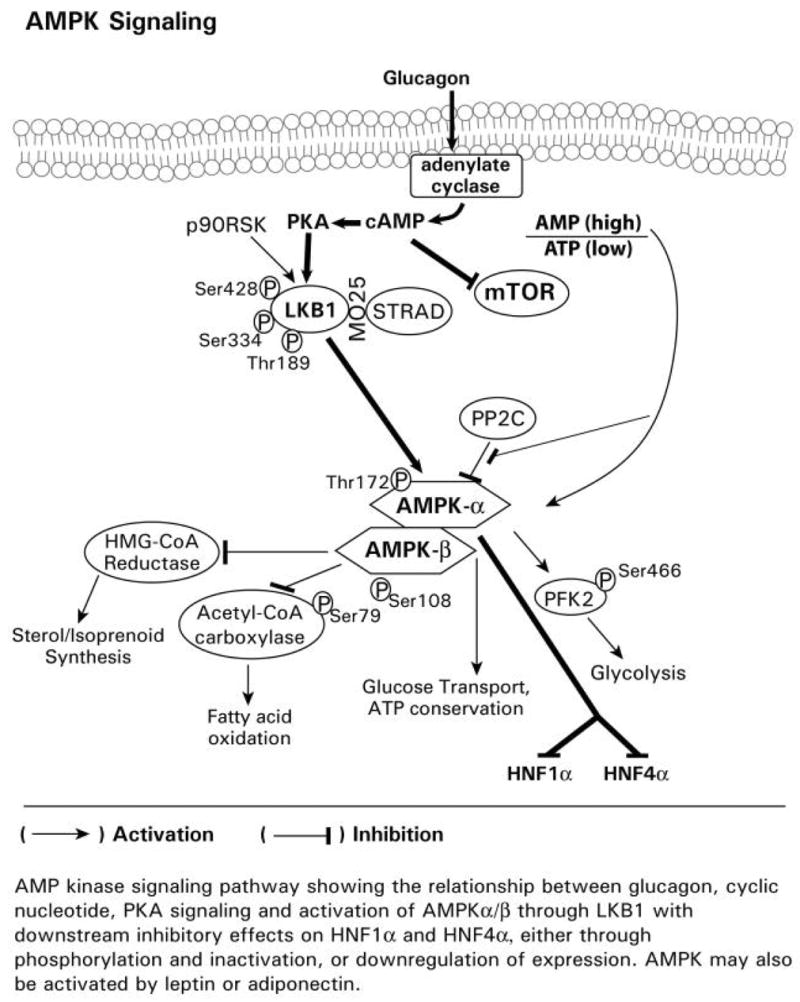
Fig. 1A Insulin-mediated signaling pathways. A diagrammatic representation of insulin and growth factor receptor mediated signaling with effects on gene transcription, through phosphorylation of the FOXO1, 3a and 4 transcription factors, and mRNA translation, through 4E-PB1, p70 S6 kinase, eIF4B, S6 ribosomal protein, and eIF4G.
Fig. 1B Glucagon-mediated signaling pathways. A diagrammatic representation of glucagon mediated signaling through the adenylate cyclase, cAMP, PKA, AMPK pathway with inhibitory effects on mTOR and the transcription factors HNF1alpha and HNF4alpha. The opposing effects of glucagon on insulin-mediated alterations in gene expression may occur through glucagon repression of insulin signaling through mTOR, which is associated with activation of PKA, the phosphorylation of LKB1, and activation of AMPK. Glucagon also represses activation of the phosphorylation of 4E-B P1 and the p70S6 kinase.
