Fig. 4.
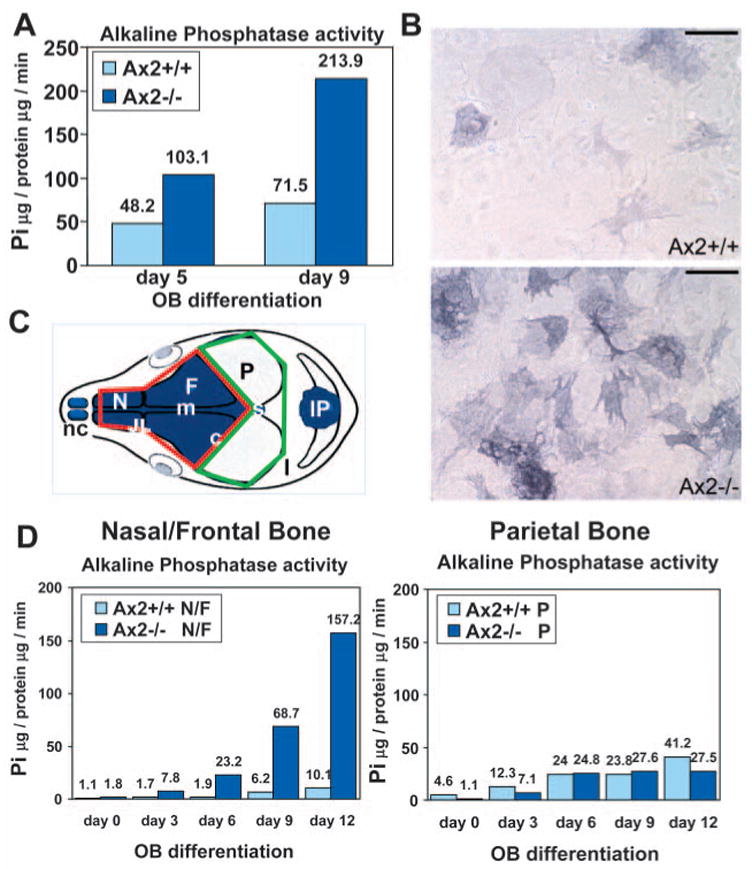
Defects of calvarial osteoblast differentiation caused by the Axin2 mutation. Primary calvarial osteoblast precursors isolated from the Axin2+/+ and Axin2−/− littermates were cultured in differentiation media for up to 9 days. Liquid (A) and histochemical (B) assays for alkaline phosphatase were performed at different time points of osteoblast (OB) differentiation as indicated. The enzyme activity is expressed as micrograms of p-nitrophenol (Pi) released per microgram of protein per minute. A diagram summarizes neural crest contribution (blue) to the skeletal elements and sutures of the mouse skull vault [diagram modified from Jiang et al. (Jiang et al., 2002)] (C). The neural crest or mesoderm-derived osteoblasts were isolated from nasal/frontal (highlighted by a red line) or parietal (highlighted by a green line) bones, respectively. c, coronal suture; F, frontal bone; IP, interparietal bone; JL, jugum limitans; l, lambdoid suture; m, metopic suture; N, nasal bone; nc, nasal cartilage; P, parietal bone; s, sagittal suture. (D) The neural crest or mesoderm-derived primary osteoblasts of Axin2+/+ and Axin2−/−were cultured in differentiation media for up to 12 days. Liquid assays for alkaline phosphatase were performed at different time points as indicated. A and D are representative of three independent experiments. Scale bar: 200 μ m in B.
