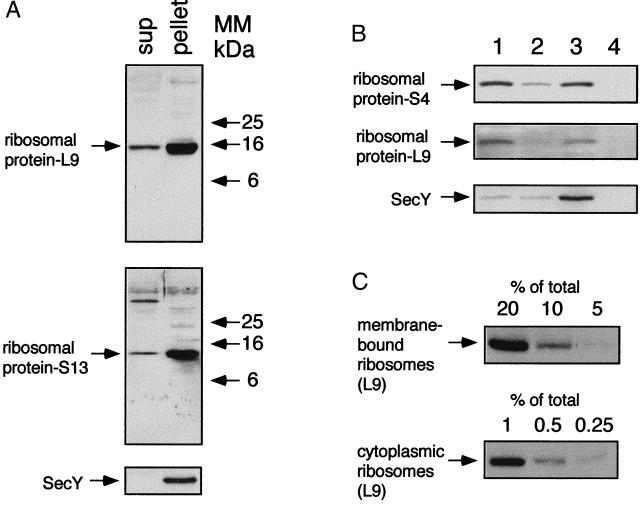
Figure 1.
Isolation of membrane-bound ribosomes. A culture of E. coli N4156 was grown in LB broth to 0.8 units of OD600. (A) Cell extracts were subjected to ultracentrifugation, and the isolated fractions (sup, 20 μg of proteins; pellet, 10 μg of proteins) were analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies against ribosomal proteins and SecY. MM, molecular mass. (B) The cellular distribution of ribosomes was studied by flotation by using the pellet that was prepared as described in A. The fractions (lane 1, bottom; lane 2, middle; lane 3, interface; lane 4, top) were analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies against ribosomal proteins and also with antibodies against the membrane protein SecY. (C) Decreasing amounts (as indicated) of proteins from fractions 3 (interface) and 1 (bottom) were analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies against the ribosomal protein L9.