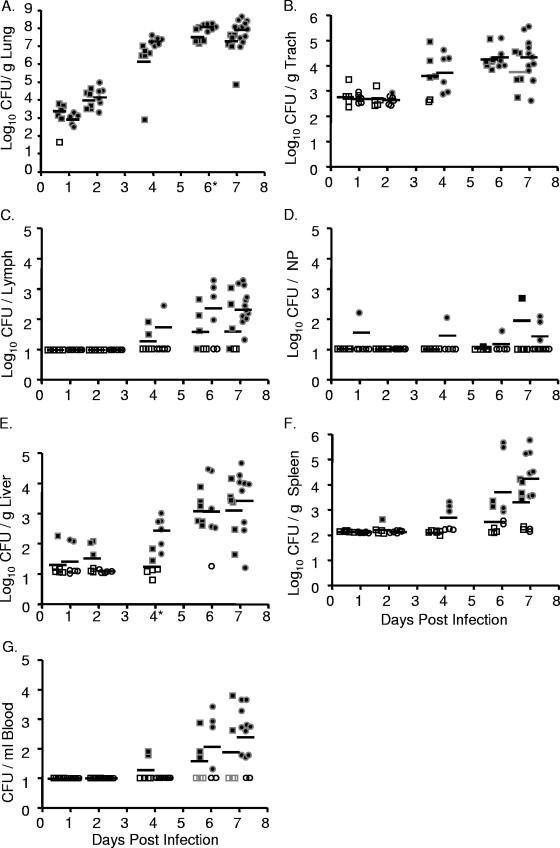
FIG. 2.
Intranasal inoculation with Y. pseudotuberculosis results in a lethal lung infection. BALB/c mice were inoculated with 300 to 500 CFU of Y. pseudotuberculosis grown at 26°C (•) or 37°C (▪). Mice were sacrificed 1, 2, 4, 6, and 7 days postinoculation and lungs (A), trachea (B), lymph nodes (C), nasopharynx (D), liver (E), spleen (F), and blood (G) were harvested, homogenized, and plated for CFU. Each dot represents data from one mouse. Open symbols indicate that bacteria were below the limit of detection (note, the limit of detection per gram of trachea recovered is generally higher than in the lungs, liver, and spleen because the weight of the trachea is smaller). Bars represent the geometric mean. *, P < 0.01 (Student's t test). NP, nasopharynx; Trach, trachea.