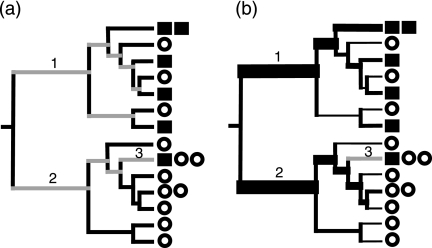
FIG. 1.
Calculation of the unweighted and the weighted UniFrac measures. Squares and circles represent sequences from two different environments. (a) In unweighted UniFrac, the distance between the circle and square communities is calculated as the fraction of the branch length that has descendants from either the square or the circle environment (black) but not both (gray). (b) In weighted UniFrac, branch lengths are weighted by the relative abundance of sequences in the square and circle communities; square sequences are weighted twice as much as circle sequences because there are twice as many total circle sequences in the data set. The width of branches is proportional to the degree to which each branch is weighted in the calculations, and gray branches have no weight. Branches 1 and 2 have heavy weights since the descendants are biased toward the square and circles, respectively. Branch 3 contributes no value since it has an equal contribution from circle and square sequences after normalization.