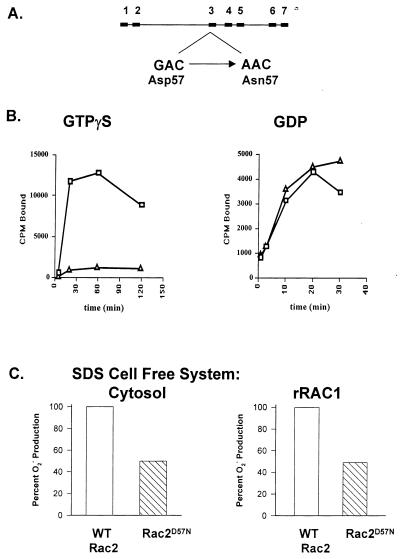
Figure 5.
(A) Molecular analysis of the Rac2 gene. Genomic DNA was prepared from both patient and control mononuclear cells and EBV-transformed B cells. Using specific primers, all six exons and exon–intron boundaries were sequenced. The genomic structure of the Rac2 locus is shown, with black boxes representing exons at their approximate position within the locus. One allele has a single-nucleotide transition, G → A, in exon 3 in the first nucleotide position of codon 57. (B) Binding of [35S]GTP[γS] and [3H]GDP to wild-type GST-Rac2 and GST-Rac2D57N. Equal amounts of wild-type and mutant Rac2 (1 μg/tube) were used in [35S]GTP[γS]- and [3H]GDP-binding experiments. These data are representative of three such experiments performed in duplicate, where the difference between replicates varied less than 5%. □, Wild-type GST-Rac2; ▵, GST-Rac2D57N. (C) Inhibition of O2− production by Rac2D57N. The production of O2− was measured as SOD-inhibitable cytochrome c reduction with the addition of 1 μg of membrane and 5 μg of cytosol from control neutrophils, 600 ng of recombinant p47-phox, 600 ng of p67-phox, and 200 ng of wild-type (WT) or D57N GST-Rac2D57N that had been preincubated with GTP[γS]. The data are presented as the percentage of O2− production in the presence of WT Rac2. A representative result from three such experiments is shown. Inhibition of Rac1⋅GTP[γS] stimulated O2− production by Rac2D57N. The production of O2− was measured as noted above except for the addition of Rac1 (173 ng) preincubated with GTP[γS] instead of cytosol in the presence of 173 ng of either WT or D57N GST-Rac2 preincubated with GTP[γS]. The data are presented as the percentage of O2− production in the presence of added recombinant WT Rac2. A representative experiment of three such experiments is shown.