Fig. 5.
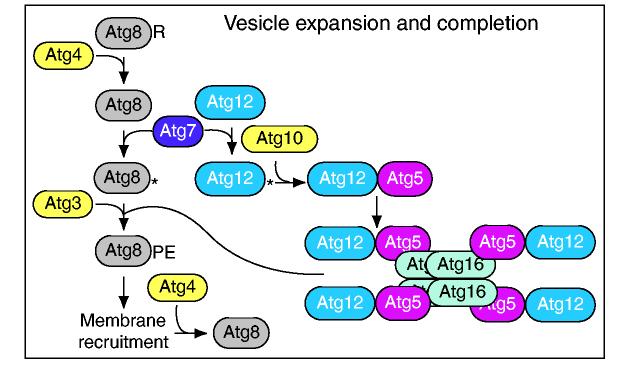
Vesicle expansion and completion. Two ubiquitin-like proteins participate in vesicle formation. The C-terminal arginine residue (R) of yeast Atg8 is removed by the Atg4 cysteine protease to reveal a glycine residue. Atg8 and Atg12 are ubiquitin-like proteins that are activated by the E1-like enzyme Atg7. Atg8 and Atg12 are then transferred to the E2-like enzymes Atg3 and Atg10 and are conjugated to phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) and Atg5, respectively. Atg8-PE becomes anchored in the membrane of the PAS and is a component of the forming and completed autophagosome or Cvt vesicle membrane. Atg12 and Atg5 bind Atg16 non-covalently and the self-interaction of Atg16 allows multimerization of the complex. A second cleavage by Atg4 releases Atg8 from the outer membrane of the completed vesicle. A similar set of reactions occurs in mammalian cells.