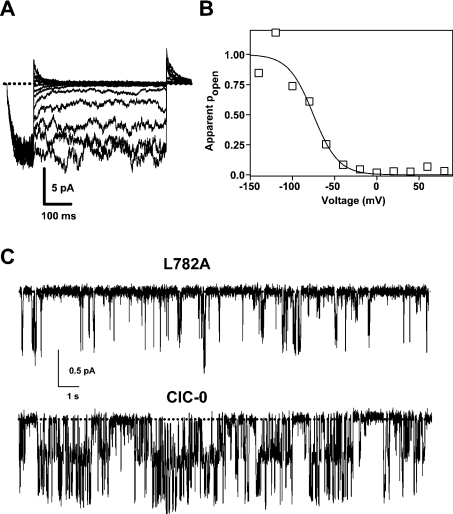
Figure 7. Mutations in the conserved segment affect the common gate.
(A) Patch–clamp traces evoked from a patch containing several ClC-0 L782A channels (average of eight recordings). After a prepulse to −140 mV the voltage was stepped up to various values ranging from +80 to −140 mV. Finally, a ‘tail’ pulse was applied to +80 mV. In (B), the normalized initial current measured during the tail pulse is plotted towards the prepulse voltage and fitted by a Boltzmann function resulting in the parameters V0.5=−75 mV, z=1.7, pmin=0.0. Comparable values for wild-type ClC-0 obtained with a longer pulse protocol to drive the slow gate into steady state are V0.5=−100 mV, z=1.8, pmin≈0.1 (results not shown). (C) The Figure shows recordings from a patch containing several L782A channels (−60 mV) and from a single-channel wild-type ClC-0 patch (−100 mV). Traces are at identical scales. The presence of more than one channel for the L782A patch was verified by pulses to more negative voltages (results not shown) at which the open probability increases markedly (see B). The short ‘burst’ duration of the mutant compared with wild-type is evident. Similar short burst durations were seen in all patches of mutant L782A (n=4). The comparably long burst of wild-type ClC-0 is well documented (e.g. [34]). The dotted line indicates the closed channel current level.