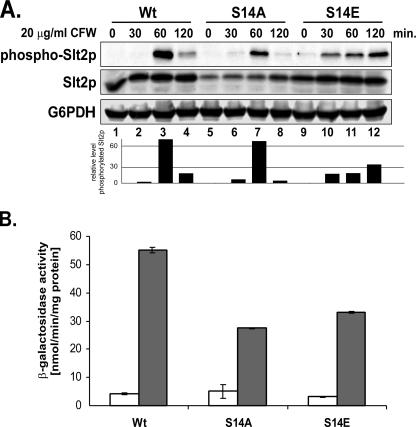
FIG. 6.
Analysis of PKC pathway activation in cdc37-S14 mutants during CFW stress. (A) Slt2p activation in cdc37-S14 mutant strains. Strains expressing wild-type Cdc37p (DH231) or the S14A (DH232) or S14E (DH233) mutant version were grown to mid-log phase in YPD medium and exposed to cell wall stress by the addition of CFW (20 μg/ml). Aliquots were taken at the indicated time points, and cell extracts were prepared and analyzed by Western blotting, using an anti-phospho-p42/44 MAPK antibody to detect phosphorylated Slt2p. The total amount of Slt2p was determined by using an anti-Slt2p antibody. Loading was assessed by means of an anti-G6PDH antibody. The same blot was used for all analyses. Bar graphs represent quantification of the level of phosphorylated Slt2p relative to total Slt2p. (B) Analysis of YIL117c-LacZ reporter gene expression in cdc37-S14 mutant strains. Strains PH301, PH302, and PH303, containing the Rlm1p-responsive YIL117c-LacZ reporter gene constructs and expressing wild-type Cdc37p and the S14A and S14E mutant versions, respectively, were grown to mid-log phase in YPD at 24°C and subsequently exposed to 20 μg/ml CFW in YPD for 2 h. Cell extracts were prepared, and β-galactosidase activity was measured (filled bars). Extracts from cells grown in the absence of CFW were used as a control (open bars). Error bars, standard deviations from the means of four experiments.