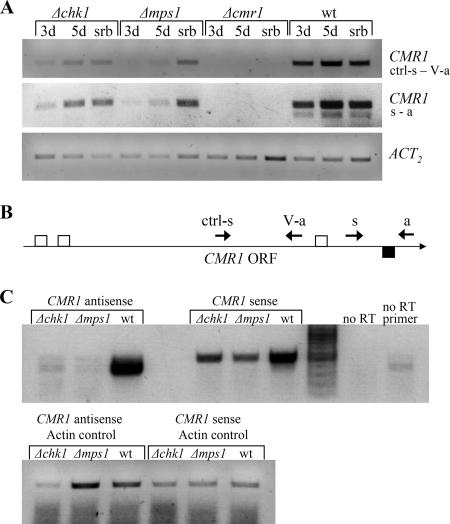
FIG. 6.
Expression of sense and antisense CMR1. (A) Semiquantitative RT-PCR analysis of CMR1 gene expression in wild type and Δchk1 and Δmpk1 mutants grown as described in the Fig. 5 legend. Polyadenylated mRNA was primed with standard oligo(dT) primer. Two primer pairs were used for the subsequent PCR: ctrl-s and V-a, and s and a (Table 1). Expression of the actin-encoding gene (ACT2) indicates relative RNA quantities in each sample. (B) Schematic representation of the primer and intron positions as related to the CMR1 open reading frame (ORF). Small arrows indicate primers used for RT and subsequent PCR. Open squares denote introns in the sense CMR1 transcript, whereas the filled square indicates an intron in the antisense CMR1. (C) Analysis of sense and antisense CMR1 transcript levels by directional cDNA synthesis. RNA used for RT-PCR was prepared from wild type and Δchk1 and Δmps1 mutants grown for 3 days in CMX, as described in the Fig. 5 legend. To examine antisense CMR1 expression, cDNA was synthesized with CMR1 primer s and actin primer act2-a to serve as an internal control. For sense CMR1 expression, RT was performed with CMR1 primer a and actin primer act2-a. Primers s and a (and act2-s and act2-a for actin) were used for the subsequent PCRs. Note that for detection of the antisense CMR1 34 PCR cycles were required, compared to 28 cycles for the sense transcript. wt, wild type.