TABLE 2.
Discriminatory power of PHAT, a binary typing method, compared to other genotyping techniques among the E. coli reference collection (ECOR) and a collection of human rectal isolates as determined by using Simpson's diversity index
| Collection (n)a | Typing method | Simpson diversity index (D)b | No. of groups | Avg no. of strains/group |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECORc (72) | PHAT | 80 | 25 | 3.1 |
| MLST | 97 | 42 | 1.5 | |
| AR | 92 | 36 | 2.0 | |
| ERIC-PCR | 97 | 43 | 1.6 | |
| ECOR isolates | PHAT | 94 | 17 | 1.4 |
| of B2 and D | MLST | 95 | 18 | 1.4 |
| lineage (26) | ||||
| Rectald (33) | MLST | 98 | 25 | 1.3 |
| PFGE | 98 | 26 | 1.2 | |
| PHAT | 98 | 26 | 1.2 |
n, number of strains in the study.
The Simpson's diversity index (D) was calculated as 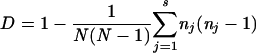 where N is the total number of strains in the sample population, s is the total number of types described, and nj is the number of strains belonging to the jth type (6).
where N is the total number of strains in the sample population, s is the total number of types described, and nj is the number of strains belonging to the jth type (6).
ECOR is a collection of 72 strains isolated from a variety of hosts and geographical locations (http://foodsafe.msu.edu/Whittam/ecor/). MLST data for ECOR isolates were obtained from www.mlst.net.
The rectal strains were randomly selected from E. coli collected from women aged 18 to 39 years with a first UTI, collected from the student health services of the University of Michigan.
