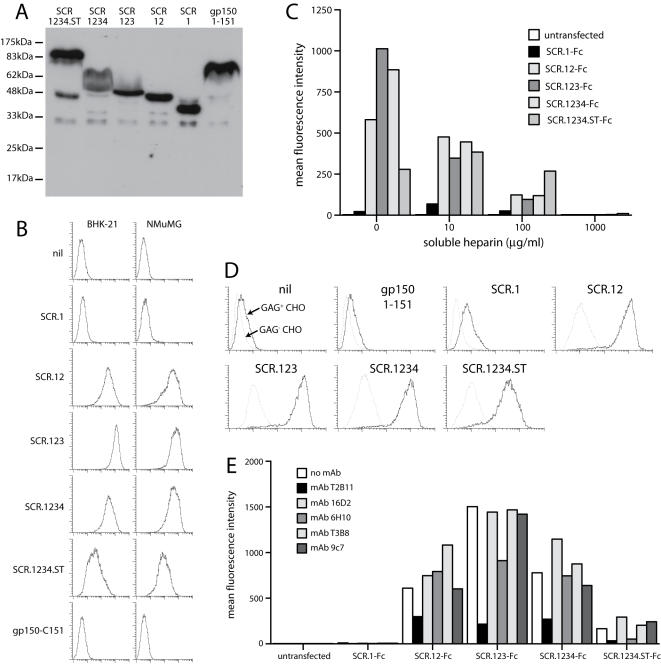
Figure 5. Heparin binding by ORF4 gene products.
A. Gp70 truncations were fused to C-terminal human IgG1 Fc and expressed by transient transfection of 293T cells. An equivalent fusion of gp150 amino acids 1-151 was used as a control. 293T cell supernatants were immunoblotted for fusion protein content with a human IgG Fc-specific pAb. B. The same supernatants were used to stain unfixed BHK-21 cells or NMuMG cells. Protein binding was assayed by flow cytometry. nil = supernatant from untransfected cells. 1 of 3 equivalent experiments is shown. C. The binding of each fusion protein to L929 cells was tested with or without soluble heparin. The fusion proteins were pre-incubated with heparin (1 h, 4°C) and then added to the cells. The graph summarizes data similar to those shown in B, from 1 of 3 equivalent experiments, each acquiring 30,000 events per sample. D. The binding of each Fc fusion protein to GAG+ or GAG− CHO cells was assayed by flow cytometry. 1 of 2 equivalent experiments is shown. E. Each ORF4-specific mAb was tested for its capacity to inhibit BHK-21 cell binding by each Fc fusion protein. The mAbs and Fc fusion proteins were incubated together (1 h, 4°C) then added to cells. The cells stained with a human IgG-Fc-specific pAb. 1 of 2 equivalent experiments is shown, again acquiring 30,000 events per sample.