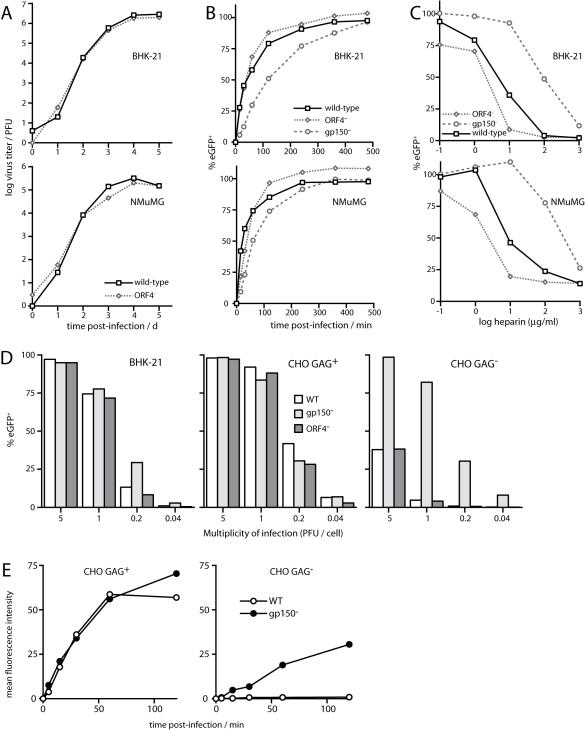
Figure 8. Infectivity of gp150 and gp70 MHV-68 knockout viruses.
A. Wild-type and ORF4-deficient (ORF4−) viruses were tested for growth in BHK-21 and NMuMG cells after low multiplicity infection (0.01 PFU/cell). The data are from 1 of 2 equivalent experiments. B. BHK-21 or NMuMG cells were exposed to wild-type, ORF4-deficient (ORF4−) or gp150-deficient (gp150−) virions for different times before washing with PBS. 18 h later viral eGFP expression was assayed by flow cytometry. Each value is expressed as a percentage of the eGFP expression of unwashed cells. The data are from 1 of 2 equivalent experiments. C. Wild-type, ORF4-deficient (ORF4−) and gp150-deficient (gp150−) virions were preincubated with heparin then added to BHK-21 or NMuMG cells. 18 h later, viral eGFP expression was assayed by flow cytometry. Each value is expressed as a percentage of the eGFP expression with untreated virus. The data are from 1 of 2 equivalent experiments. D. BHK-21, CHO GAG+ or CHO GAG− cells were infected overnight with wild-type (WT), gp150-deficient (gp150−) or ORF4-deficient viruses (ORF4−) in the presence of 10 µg/ml phosphonoacetic acid to inhibit any viral spread. Each virus expressed eGFP from an HCMV IE1 promoter in the BAC cassette at the left end of the genome. The number of infected cells was assessed by flow cytometric counting of eGFP+ cells. The data are from 1 of 2 equivalent experiments. E. CHO GAG+ or CHO GAG− cells were exposed to gp150+ (WT) or gp150− virions that were fluorescent by virtue of an eGFP tag on glycoprotein M. At the times shown, the cells were washed with PBS to remove unbound virions. Virion binding was then quantitated by flow cytometry. The data are from 1 of 2 equivalent experiments.