Figure 5.
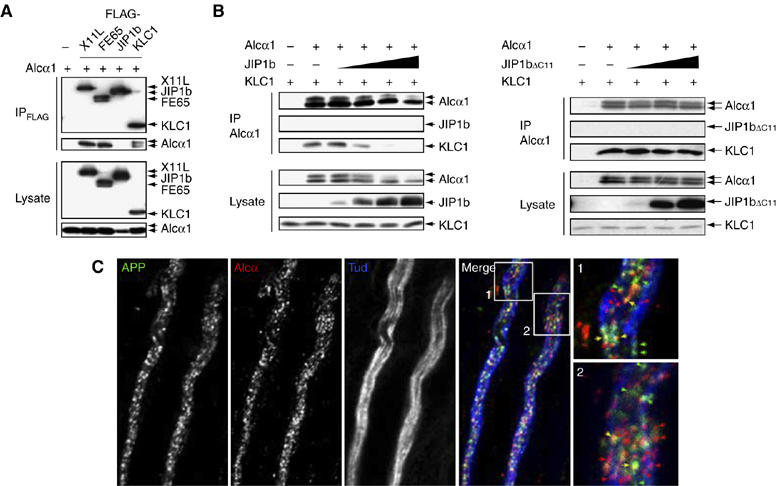
Separate transport of APP- and Alcα-containing vesicles by kinesin-1. (A) Interaction of Alcα1 with adaptor proteins. HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with pcDNA3-hAlcα1 (+) in the presence of pcDNA3-FLAG-hX11L, pcDNA3-N-FLAG-FE65, pcDNA3-FLAG-JIP1b, pcDNA3.1-FLAG-mKLC1, or vector alone (−). Cells were lysed and immunoprecipitated with the anti-FLAG M2 antibody. Immunoprecipitates (IP) and cell lysates (Lysate) were analyzed by Western blotting with the M2 and anti-Alcα UT83 antibodies. (B) Effect of wild-type and mutant JIP1b on the Alcα1-KLC1 interaction. (Left) HEK293 cells were transiently cotransfected with pcDNA3.1-mKLC1 (0.5 μg), pcDNA3-hAlcα1 (0.5 μg), and 0, 0.05, 0.2, 0.7, or 2.2 μg pcDNA3-JIP1b. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with an anti-Alcα (UT83) antibody and immunoprecipitates (IP) and cell lysates (Lysate, 10 μg protein) were analyzed by Western blotting with the UT83, UT72, and UT109 antibodies. (Right) Cells were similarly cotransfected using 0, 0.2, 0.7, or 2.2 μg pcDNA3.1-JIP1bΔC11. The UT83 immunoprecipitate (IP) and cell lysate (Lysate, 10 μg protein) were analyzed as described above. Transfection with 0.5 μg plasmid (+) or vector alone (−) is indicated. (C) APP- and Alcα-containing vesicles in adult mouse sciatic nerve. Isolated axons of sciatic nerves were immunostained with anti-APP (αAPP/C, green), anti-Alcα (co190, red), and anti-neuronal Class III β-tubulin (TUJ1, blue; showing axons) antibodies. Signals are merged and magnified in the lower panels. Yellow arrows indicate vesicles containing both APP and Alcα. Scale bar, 5 μm.
