Figure 4.
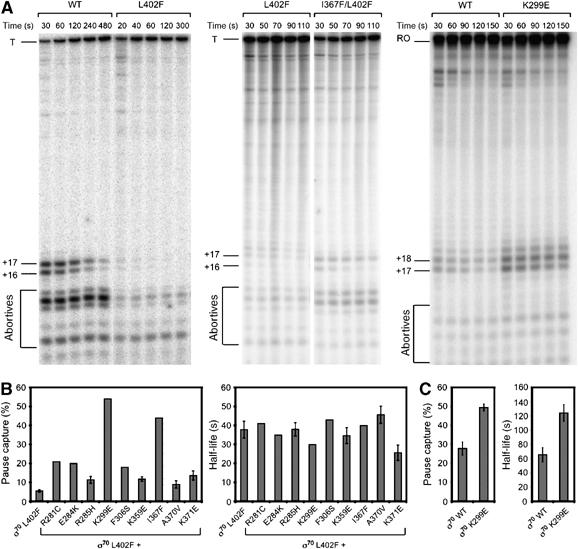
Substitutions in the σ70 NCR enhance pausing at λPR′ and at placUV5. (A) Single-round in vitro transcription time-course assays using a PR′ template (left and middle panels) or a placUV5 template (right panel) and RNAP reconstituted with the indicated σ70 proteins. Aliquots of single reactions were removed and stopped at the indicated time points after transcription was initiated. The RNA was labeled internally with [α-32P]UTP (middle and right panels) or end-labeled with [γ-32P]ATP (left panel). +16 and +17, 16- and 17-nt RNA species, respectively, produced from the λPR′ template; T, 194-nt terminated transcript produced from the λPR′ template; +17 and +18, 17- and 18-nt RNA species, respectively, produced from the placUV5 template; RO, 96-nt runoff transcript produced from the placUV5 template. A faint 18-nt RNA species was also observed during time courses with the λPR′ template when the RNA was internally labeled. This is likely the result of nucleotide deprivation at U19 under conditions where the UTP concentration was reduced to improve incorporation of [α-32P]UTP, and has been observed previously under similar reaction conditions (Ko et al, 1998). (B, C) Effects of substitutions on pause capture and pause half-life. The percentage of elongation complexes paused (100 (16-nt+17-nt)/(16-nt+17-nt+T) or 100 (17-nt+18-nt)/(17-nt+18-nt+T)) was approximated at each time point, plotted, and fit to the exponential equation Y=Y0e−kt (Supplementary Figure S1). Exponential equations were solved to obtain pause capture (left panels) and half-life (right panels) values for each holoenzyme. Pause capture was approximated by extrapolating the equations to t=0. Error bars represent standard deviations from at least three separate experiments. In cases where error bars are not shown, the mutants were assayed twice, with similar results.
