Figure 5.
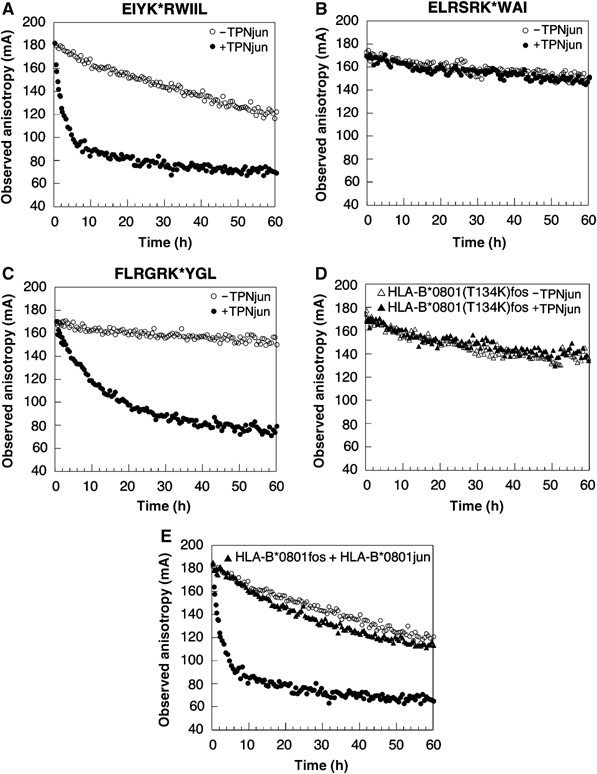
Effect of TPNjun on the kinetics of peptide dissociation. (A) Dissociation of EIYK*RWIIL was monitored as described in Figure 1B: HLA-B*0801fos alone (40 nM) (○) and in the presence of TPNjun (400 nM) (•). Data points were collected at various time points over a period of 166 h (−TPN) or continuously for 60 h (+TPN). (B) As described in Figure 1B for ELRSRK*WAI: HLA-B*0801fos alone (40 nM) (○) and in the presence of TPNjun (400 nM) (•). Data points were collected at various time points over a period of 576 h. (C) As described in Figure 1B for FLRGRK*YGL: HLA-B*0801fos alone (40 nM) (○) and in the presence of TPNjun (400 nM) (•). Data points were collected at various time points over a period of 546 h (−TPN) or continuously for 89 h (+TPN). (D) Dissociation of FLRGRK*YGL from HLA-B*0801(T134K)fos (40 nM) in the absence (▵) or presence (▴) of TPNjun (400 nM) was monitored as described in Figure 1B. Data points were collected continuously for 60 h. (E) Dissociation of EIYK*RWIIL from HLA-B*0801fos (40 nM) in the presence of HLA-B*0801jun/ELRSRKWAI (400 nM) (▴) was monitored as described in Figure 1B. Data points were collected continuously for 60 h. The decay curves shown in (A) are included for comparison purposes.
