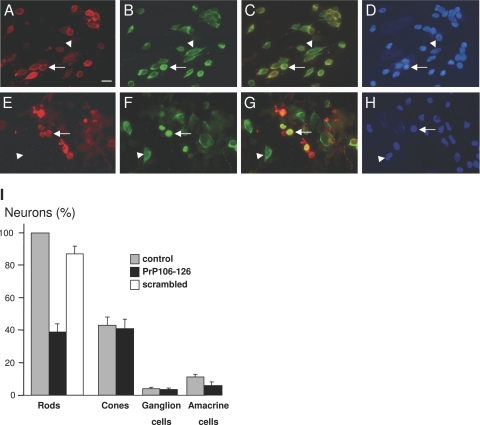
Figure 6.
The prion peptide PrP106-126 induced rod cell death in mixed retinal culture. Control (A–D) and PrP106-126-treated retinal cell cultures (E–H) that were immunolabeled for rhodopsin (red in A, C, E, G) and arrestin (green in B, C, F, G) and stained with the nuclear dye 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (D, H). Rod photoreceptors exhibited rhodopsin labeling of plasma membranes and arrestin staining of the cytoplasm (arrow in A–D), whereas cone photoreceptors were specifically identified by the arrestin antibody (arrowheads in A–H). Note in the PrP106-126 treated cultures that some structures showed an abnormally intense rhodopsin immunolabeling (arrow in E–H) but lacked the 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole nuclear staining. I: Quantification of retinal cells in control retinal cell cultures (control), cultures treated with the PrP106-126 peptide (PrP106-126), and culture treated with a scrambled peptide. The differences in rod and amacrine cell survival were statistically significant (P < 0.05). All measures were normalized to the number of rods in the control conditions and provided as SEM with n = 3 for both conditions. The scale bar in A represents 10 μm.