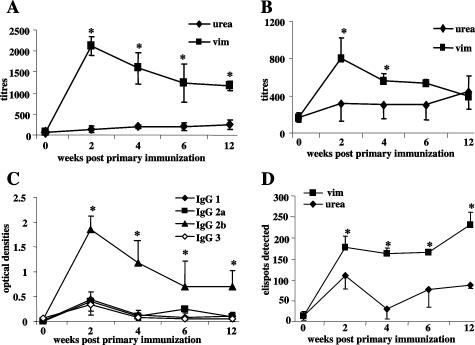
Figure 1.
Antibody and cytokine production in vimentin-immunized mice. C57BL/6 mice were immunized with 400 μg of vimentin emulsified in CFA followed by a booster of 400 μg of vimentin alone 1 week later. Controls received 100 μl of 6 mol/L urea (vehicle) in CFA. ELISA was used to determine titers of IgG (A) and IgM (B) AVA at 2 to 12 weeks after the first injection. IgG subclasses of AVA were determined in C. Points represent means and standard deviations of four mice per group. *P < 0.05 for differences between vimentin-immunized mice and controls in A and B and for differences between IgG2b titers and other subclasses in C. D: Cytokine production by splenocytes from vimentin-immunized mice assessed by ELISPOT. Spleens from mice immunized with vim/CFA (vim) or urea/CFA (urea) were removed at time 0 and 2 to 12 weeks after the first injection, and splenocytes were prepared and cultured with murine vimentin to determine production of IFN-γ (see Materials and Methods). In brief, 106 splenocytes were cultured with vimentin, urea, or concanalavin-A (not shown) in vitro, in wells coated with mAb to IFN-γ (D). After 48 hours, the cells were lysed with distilled water and ELISPOTs developed using antibodies to appropriate biotinylated mAb. Points represent means and standard deviations of four mice per group. *P < 0.05 for differences between vimentin- or urea-immunized mice.