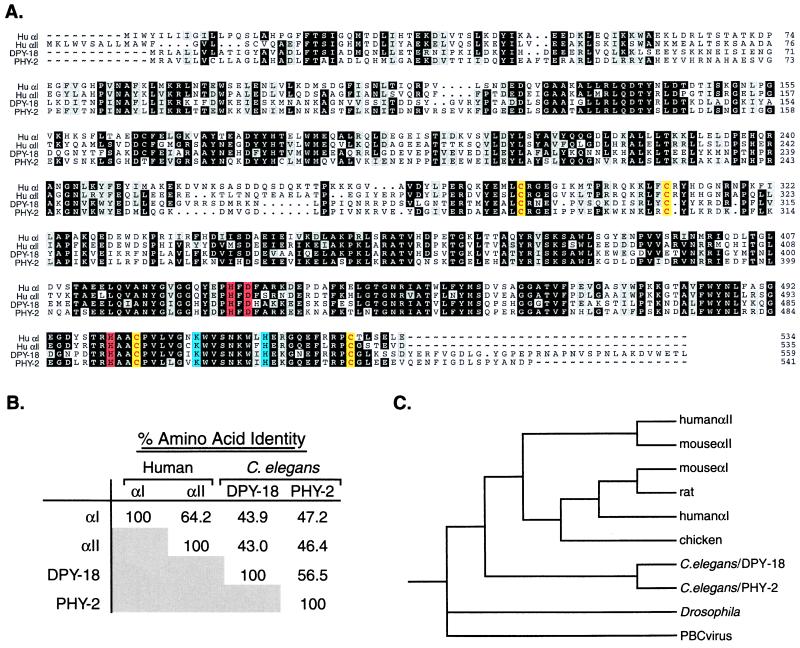
Figure 1.
Sequence analysis of prolyl 4-hydroxylase α subunits. (A) Alignment of amino acid sequences of human αI (accession no. M24486), human αII (accession no. U90441), C. elegans DPY-18 (accession no. AL031635), and C. elegans PHY-2 (accession no. Z69637), by using the pileup program of the GCG-Wisconsin package. The human αI sequence is the form encoded by the more 5′ of the two alternatively spliced exons (43, 44). The DPY-18 sequence differs at amino acids 308–312 from that reported (18). Our sequence was confirmed by sequencing cDNA yk339d8 (provided by Y. Kohara, National Institute of Genetics, Mishiwa, Japan) and N2 genomic DNA. Amino acids conserved among at least three of the four proteins are shaded: identity, black; similarity, gray ({I, L, V}; {F, W, Y}; {D, E}; {K, R}; {S, T}). Amino acids essential for enzymatic activity are shown in color: Fe2+-binding residues, red; amino acids involved in decarboxylation of α-ketoglutarate, blue; cysteine residues critical for α/β complex formation and enzymatic activity, yellow. (B) Amino acid identity among the human and C. elegans prolyl 4-hydroxylase α subunits as calculated by the distances program of GCG-Wisconsin package. (C) Phylogenetic tree of prolyl 4-hydroxylase α subunits (45–50). Phylogenetic analysis was performed by using the programs pairwise of GCG and paup. The tree was generated with the paup parsimony analysis by using an exhaustive tree search rooted with the Paramecium Borella Chlorella (PBC) viral sequence. This tree is the same as that generated with a distance algorithm (data not shown).