Abstract
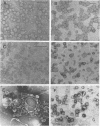
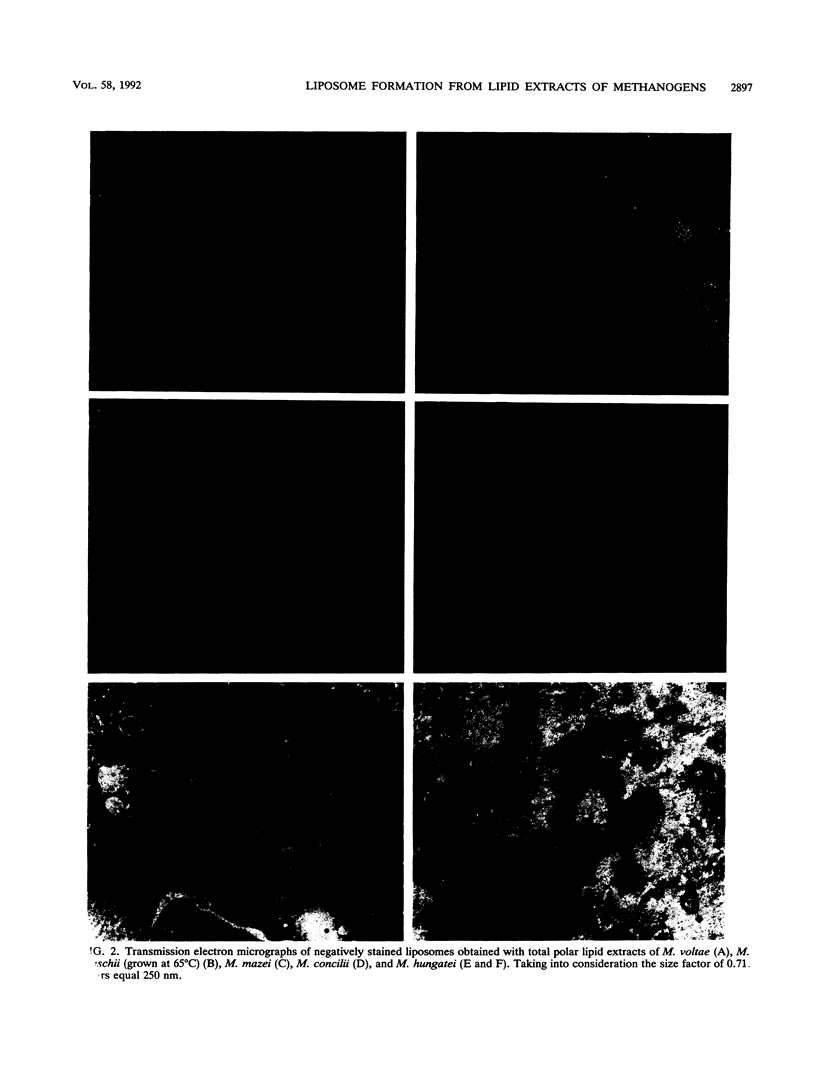
Unilamellar liposomes were formed by controlled detergent dialysis of mixed micelles consisting of acetone-insoluble total polar lipids extracted from various methanogens and the detergent n-octyl-beta-D-glucopyranoside. The final liposome populations were studied by dynamic light scattering and electron microscopy. Unilamellar liposomes with mean diameters smaller than 100 nm were obtained with lipid extracts of Methanococcus voltae, Methanosarcina mazei, Methanosaeta concilii, and Methanococcus jannaschii (grown at 50 degrees C), whereas larger (greater than 100-nm) unilamellar liposomes were obtained with lipid extracts of M. jannaschii grown at 65 degrees C. These liposomes were shown to be closed intact vesicles capable of retaining entrapped [14C]sucrose for extended periods of time. With the exception of Methanospirillum hungatei liposomes, all size distributions of the different liposome populations were fairly homogeneous.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balch W. E., Fox G. E., Magrum L. J., Woese C. R., Wolfe R. S. Methanogens: reevaluation of a unique biological group. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Jun;43(2):260–296. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.2.260-296.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breuil C., Patel G. B. Composition of Methanospirillum hungatii GP1 during growth on different media. Can J Microbiol. 1980 May;26(5):577–582. doi: 10.1139/m80-102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. S., Barton P. G., Brown D., Kates M. Osmometric and microscopic studies on bilayers of polar lipids from the extreme halophile, Halobacterium cutirubrum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jun 13;352(2):202–217. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90212-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBose C. D., Roberts M. F. The interaction of dialkyl ether lecithins with phospholipase A2 (Naja naja naja). J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6327–6334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degani H., Danon A., Caplan S. R. Proton and carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the polar lipids of Halobacterium halobium. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 15;19(8):1626–1631. doi: 10.1021/bi00549a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elferink M. G., de Wit J. G., Demel R., Driessen A. J., Konings W. N. Functional reconstitution of membrane proteins in monolayer liposomes from bipolar lipids of Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1375–1381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante G., Brisson J. R., Patel G. B., Ekiel I., Sprott G. D. Structures of minor ether lipids isolated from the aceticlastic methanogen, Methanothrix concilii GP6. J Lipid Res. 1989 Oct;30(10):1601–1609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante G., Richards J. C., Sprott G. D. Structures of polar lipids from the thermophilic, deep-sea archaeobacterium Methanococcus jannaschii. Biochem Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;68(1):274–283. doi: 10.1139/o90-038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazrak T., Milon A., Wolff G., Albrecht A. M., Miehé M., Ourisson G., Nakatani Y. Comparison of the effects of inserted C40- and C50-terminally dihydroxylated carotenoids on the mechanical properties of various phospholipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Sep 18;903(1):132–141. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90163-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenberg D., Barenholz Y. Liposomes: preparation, characterization, and preservation. Methods Biochem Anal. 1988;33:337–462. doi: 10.1002/9780470110546.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo S. L., Chang E. L. Purification and characterization of a liposomal-forming tetraether lipid fraction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Feb 28;167(1):238–243. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91756-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimms L. T., Zampighi G., Nozaki Y., Tanford C., Reynolds J. A. Phospholipid vesicle formation and transmembrane protein incorporation using octyl glucoside. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):833–840. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross N. W., Levitan R., Labelle J., Schneider H. Protein and other compositional differences of the extracellular material from slimy and non-slimy colonies of non-mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Jul 1;65(3):257–260. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90223-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwendener R. A., Asanger M., Weder H. G. n-Alkyl-glucosides as detergents for the preparation of highly homogeneous bilayer liposomes of variable sizes ( 60-240 nm phi) applying defined rates of detergent removal by dialysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jun 16;100(3):1055–1062. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91930-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprott G. D., Ekiel I., Dicaire C. Novel, acid-labile, hydroxydiether lipid cores in methanogenic bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13735–13740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprott G. D., Meloche M., Richards J. C. Proportions of diether, macrocyclic diether, and tetraether lipids in Methanococcus jannaschii grown at different temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(12):3907–3910. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.12.3907-3910.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]