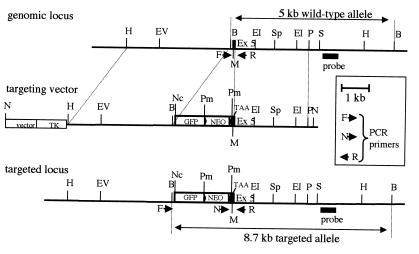
Figure 1.
Murine Fhit genomic locus, targeting and screening strategy. The top line represents the Fhit genomic locus surrounding exon 5. The middle line depicts the targeting vector with a 6.6-kb HindIII (H)–PstI (P) fragment with a termination codon introduced into exon 5. The targeted locus after homologous recombination is shown at the bottom with the probe used for Southern blot screening of ES colony and progeny DNA after BamHI (B) cleavage. Positions of the primers used for PCR amplification of progeny DNA, to identify wild-type (F,R) and targeted (N,R) alleles, are shown. Restriction enzyme sites are shown for EcoRV (EV), EcoRI (E1), SphI (Sp), SacI (S), NotI (N), NcoI (Nc), and Pme1 (Pm). The 5′→3′ sequences of the three primers F, R, and N are, respectively: CTTGAATCTAGGCTGCATTCTAGCGAG, GATTCCTTGCTTACCTTTTGGGGATGG, and TGGGCTCTATGGCTTCTGAGGC. The first reaction product is a wild-type fragment of ≈450 bp containing exon 5; the second product is a mutant fragment of ≈280 bp spanning from the Neo selection gene to intron 5. PCR conditions were: denaturation 94°C, 30 s; annealing 62°C, 30 s; elongation 72°C, 30 s; 35 cycles.