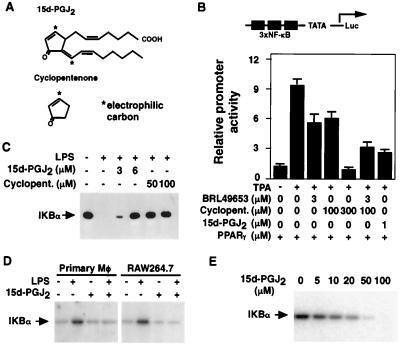
Figure 2.
Effects of 15d-PGJ2 on activity of IKK and IκB degradation. (A) Structures of 15d-PGJ2 (11-oxoprosta-5Z,9,12E,14Z-tetraen-1-oic acid) and cyclopentenone. The positions of chemically reactive, electrophilic carbons are indicated by asterisks. (B) Inhibition of NF-κB by cyclopentenone and the PPARγ-specific ligand BRL49653 is additive in the presence of PPARγ. HeLa cells were transfected with the (NF-κB)3-TATA-Luc reporter and β-actin-β-gal (1 μg each), with pCMX-PPARγ (200 ng). Transfected cells were treated for 16 h with TPA (100 nM) and other additions as indicated. (C) 15d-PGJ2 and cyclopentenone inhibit degradation of IκB in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. RAW cells were treated with 15d-PGJ2 or cyclopentenone for 1 h. Cells were stimulated with LPS (1 μg/ml) for 30 min, and whole cell extracts were assayed for IκBα by Western blotting. (D) 15d-PGJ2 inhibits IKK activity. PPARγ-negative resident murine peritoneal macrophages and RAW264.7 cells were incubated with 15d-PGJ2 (6 μM) as indicated for 1 h and then stimulated with LPS (1 μg/ml). Whole cell extracts were prepared 10 min later, and IKK activity was assayed by using GST-IKBα (1–54) as a substrate. (E) 15d-PGJ2 inhibits kinase activity of purified IKK. IκBα (1–54) was incubated with purified IKK and [γ-32P]ATP in the presence of the indicated concentrations of 15d-PGJ2 and 0.1 mM dithiothreitol. Incorporation of 32P was determined by SDS/PAGE and phosphorimaging.