Fig. 3.
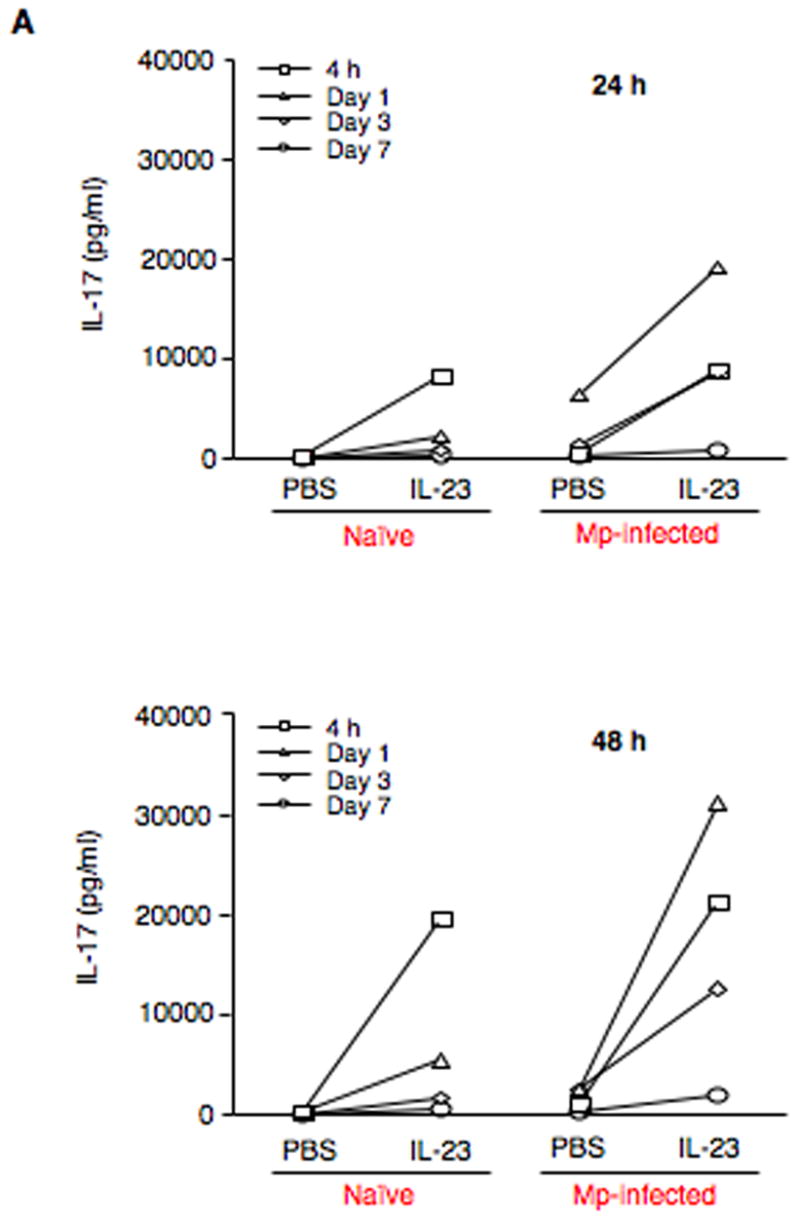
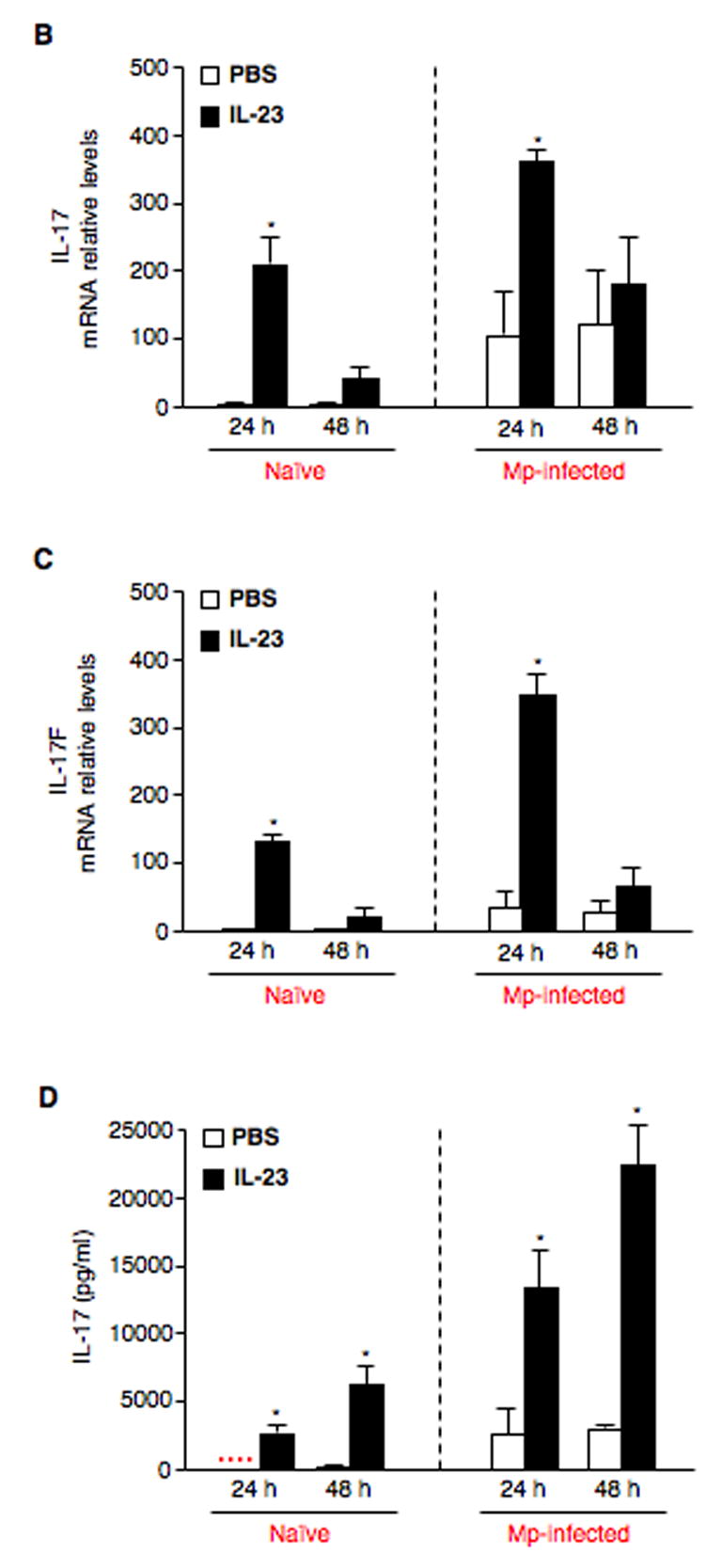
IL-23 increases expression of IL-17 family members by pulmonary CD4+ T cells. (A) Pulmonary CD4+ T cells isolated from naïve (saline-treated) and Mp-infected mice at 4 h, days 1, 3 and 7 were incubated in the absence (PBS) or presence of 10 ng/ml rmIL-23 for 24 h or 48 h. IL-17 protein in cell supernatants was measured by ELISA. To further confirm the findings in Fig. 3A, pulmonary CD4+ T cells from naïve (saline-treated) and Mp-treated mice at 24 h were incubated in the absence (PBS) or presence of 10 ng/ml rmIL-23 for 24 h or 48 h. Relative mRNA levels of IL-17 (B) and IL-17F (C), and protein levels of IL-17 (D) are expressed as means ± SEM from three independent replicates. *p < 0.05, matched-pairs t test comparing PBS with IL-23 treatment. Dotted line = undetectable level.
