Abstract
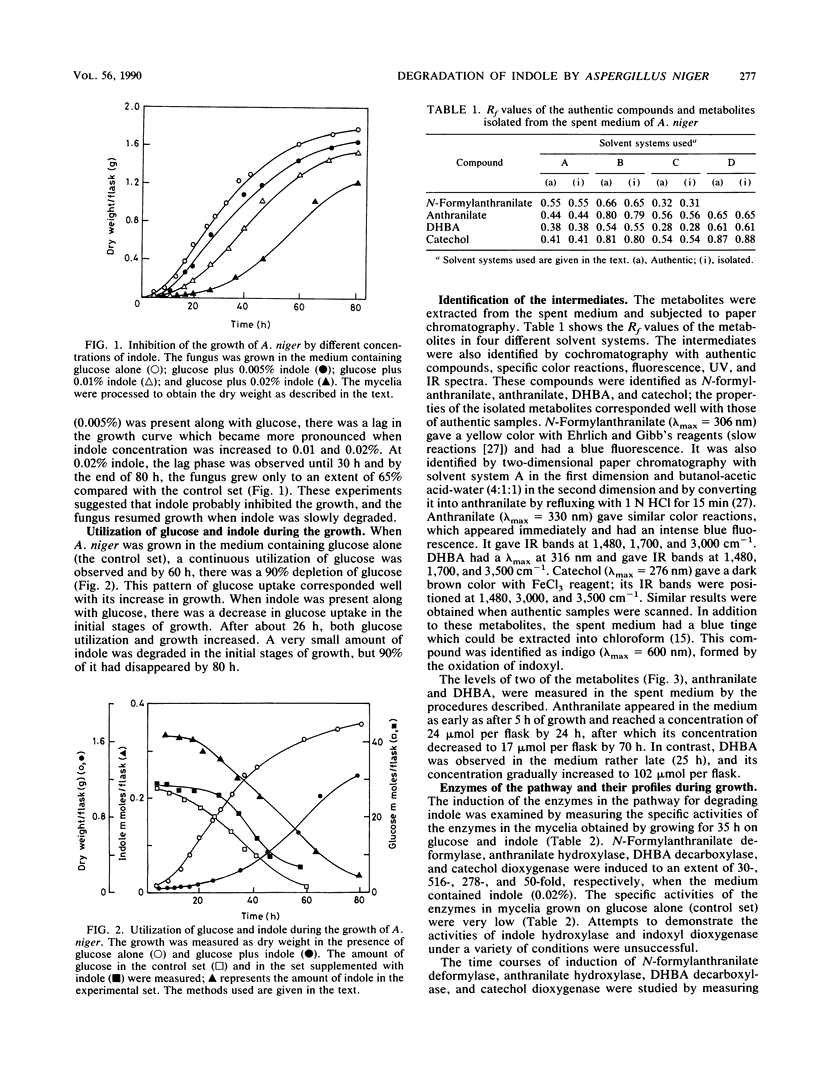
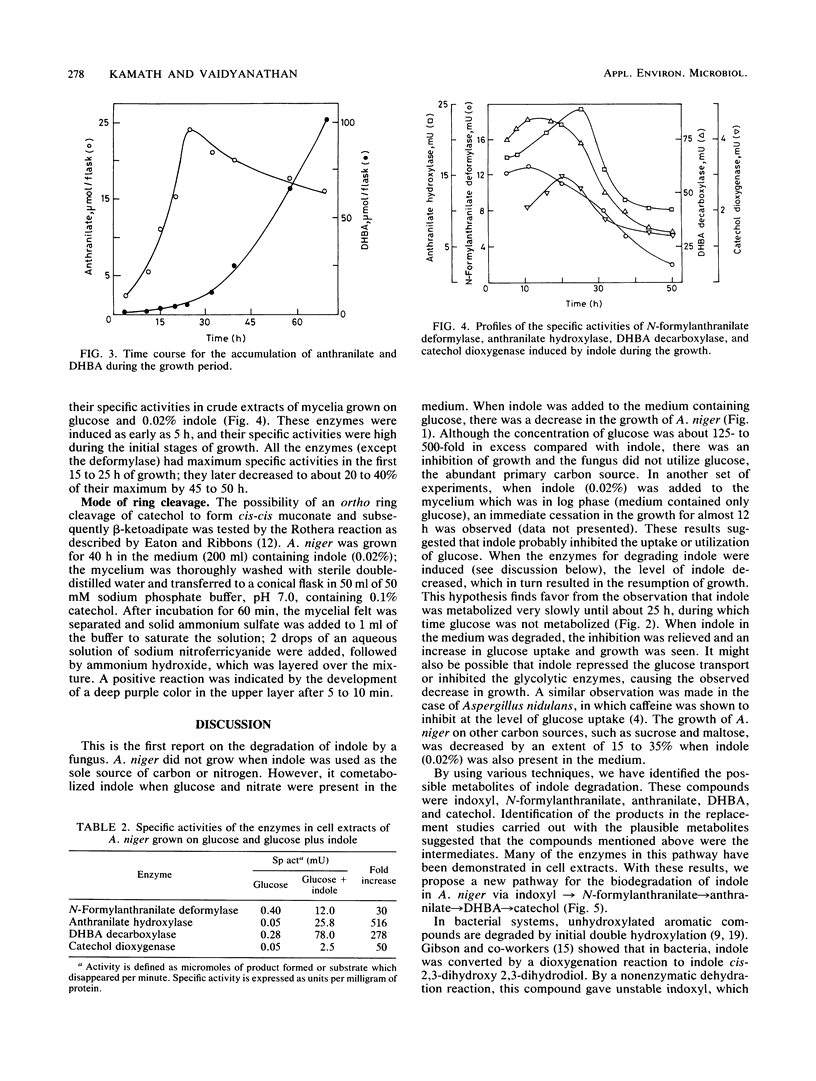
Indole and its derivatives form a class of toxic recalcitrant environmental pollutants. The growth of Aspergillus niger was inhibited by very low concentrations (0.005 to 0.02%) of indole, even when 125- to 500-fold excess glucose was present in the medium. When 0.02% indole was added, the fungus showed a lag phase for about 30 h and the uptake of glucose was inhibited. Indole was metabolized by a new pathway via indoxyl (3-hydroxyindole), N-formylanthranilic acid, anthranilic acid, 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid, and catechol, which was further degraded by ortho cleavage. The enzymes N-formylanthranilate deformylase, anthranilate hydroxylase, 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate decarboxylase, and catechol dioxygenase were induced by indole as early as after 5 h of growth, and their activities were demonstrated in a cell-free system.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acheson R. M., Nwankwo J. O. The metabolism of some 1-hydroxylated indoles in the rat. Xenobiotica. 1984 Nov;14(11):877–883. doi: 10.3109/00498258409151486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arcos J. C., Myers S. C., Neuburger B. J., Argus M. F. Comparative effects of indole and aminoacetonitrile derivatives on dimethylnitrosamine-demethylase and aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase activities. Cancer Lett. 1980 Apr;9(2):161–167. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(80)90120-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BYRDE R. J., HARRIS J. F., WOODCOCK D. Fungal detoxication, the metabolism of -(2-naphthyloxy)-n-alkylcarboxylic acids by Aspergillus niger. Biochem J. 1956 Sep;64(1):154–160. doi: 10.1042/bj0640154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry D. F., Madsen E. L., Bollag J. M. Conversion of indole to oxindole under methanogenic conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jan;53(1):180–182. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.1.180-182.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan R. L., Lewis D. F. Caffeine inhibition of aflatoxin synthesis: probable site of action. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jun;47(6):1216–1220. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.6.1216-1220.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson J. R., Yokoyama M. T., Dickinson E. O. Induction of pulmonary edema and emphysema in cattle and goats with 3-methylindole. Science. 1972 Apr 21;176(4032):298–299. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4032.298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chipley J. R., Uraih N. Inhibition of Aspergillus growth and aflatoxin release by derivatives of benzoic acid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Aug;40(2):352–357. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.2.352-357.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge R. H., Cerniglia C. E., Gibson D. T. Fungal metabolism of biphenyl. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 15;178(1):223–230. doi: 10.1042/bj1780223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton R. W., Ribbons D. W. Metabolism of dibutylphthalate and phthalate by Micrococcus sp. strain 12B. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):48–57. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.48-57.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton R. W., Timmis K. N. Characterization of a plasmid-specified pathway for catabolism of isopropylbenzene in Pseudomonas putida RE204. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):123–131. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.123-131.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensley B. D., Ratzkin B. J., Osslund T. D., Simon M. J., Wackett L. P., Gibson D. T. Expression of naphthalene oxidation genes in Escherichia coli results in the biosynthesis of indigo. Science. 1983 Oct 14;222(4620):167–169. doi: 10.1126/science.6353574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evarts R. P., Mostafa M. H. Effects of indole and tryptophan on cytochrome P-450, dimethylnitrosamine demethylase, and arylhydrocarbon hydroxylase activities. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Mar 1;30(5):517–522. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90638-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florin I., Rutberg L., Curvall M., Enzell C. R. Screening of tobacco smoke constituents for mutagenicity using the Ames' test. Toxicology. 1980;15(3):219–232. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(80)90055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujioka M., Wada H. The bacterial oxidation of indole. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 16;158(1):70–78. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90073-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond A. C., Carlson J. R., Breeze R. G. Indole toxicity in cattle. Vet Rec. 1980 Oct 11;107(15):344–346. doi: 10.1136/vr.107.15.344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAKOBY W. B. Kynurenine formamidase from Neurospora. J Biol Chem. 1954 Apr;207(2):657–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamath A. V., Dasgupta D., Vaidyanathan C. S. Enzyme-catalysed non-oxidative decarboxylation of aromatic acids: I. Purification and spectroscopic properties of 2,3 dihydroxybenzoic acid decarboxylase from Aspergillus niger. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 May 29;145(1):586–595. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91361-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin D. A., Mastromarino A. J., Jones R. D., Stroehlein J. R., Lorentz O. Fecal skatole and indole and breath methane and hydrogen in patients with large bowel polyps or cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1985;109(2):135–141. doi: 10.1007/BF00391888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King L. J., Parke D. V., Williams R. T. The metabolism of [2-14C] indole in the rat. Biochem J. 1966 Jan;98(1):266–277. doi: 10.1042/bj0980266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishore G., Sugumaran M., Vaidyanathan C. S. Metabolism of DL-(+/-)-phenylalanine by Aspergillus niger. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):182–191. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.182-191.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunapuli S. P., Vaidyanathan C. S. Purification and Characterization of a New Indole Oxygenase from the Leaves of Tecoma stans L. Plant Physiol. 1983 Jan;71(1):19–23. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen E. L., Francis A. J., Bollag J. M. Environmental factors affecting indole metabolism under anaerobic conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jan;54(1):74–78. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.1.74-78.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melo A. A., Querol C. B., Henriques A. T., Henriques J. A. Cytostatic, cytotoxic and mutagenic effects of voacristine, an indole alkaloid in wild-type and repair-deficient yeasts. Mutat Res. 1986 Jul;171(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(86)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mostafa M. H., Ruchirawat M., Weisburger E. K. Comparative studies on the effects of various microsomal enzyme inducers on the N-demethylation of dimethylnitrosamine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 15;30(14):2007–2011. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90212-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAIR P. M., VAIDYANATHAN C. S. A COLORIMETRIC METHOD FOR DETERMINATION OF PYROCATECHOL AND RELATED SUBSTANCES. Anal Biochem. 1964 Mar;7:315–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAIR P. M., VAIDYANATHAN C. S. AN INDOLE OXIDASE ISOLATED FROM THE LEAVES OF TECOMA STANS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Mar 9;81:496–506. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90134-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochiai M., Wakabayashi K., Sugimura T., Nagao M. Mutagenicities of indole and 30 derivatives after nitrite treatment. Mutat Res. 1986 Dec;172(3):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(86)90056-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMOGYI M. Notes on sugar determination. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):19–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley A. R., Spray R. S. The Photoelectric Determination of Indole in Bacterial Cultures. J Bacteriol. 1941 Feb;41(2):251–257. doi: 10.1128/jb.41.2.251-257.1941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance W. A., Okamoto H. S., Wang Y. Y. Structure-activity relationships of nitro and methyl-nitro derivatives of indoline, indole, indazole and benzimidazole in Salmonella typhimurium. Mutat Res. 1986 Mar;173(3):169–176. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(86)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


