Figure 1.
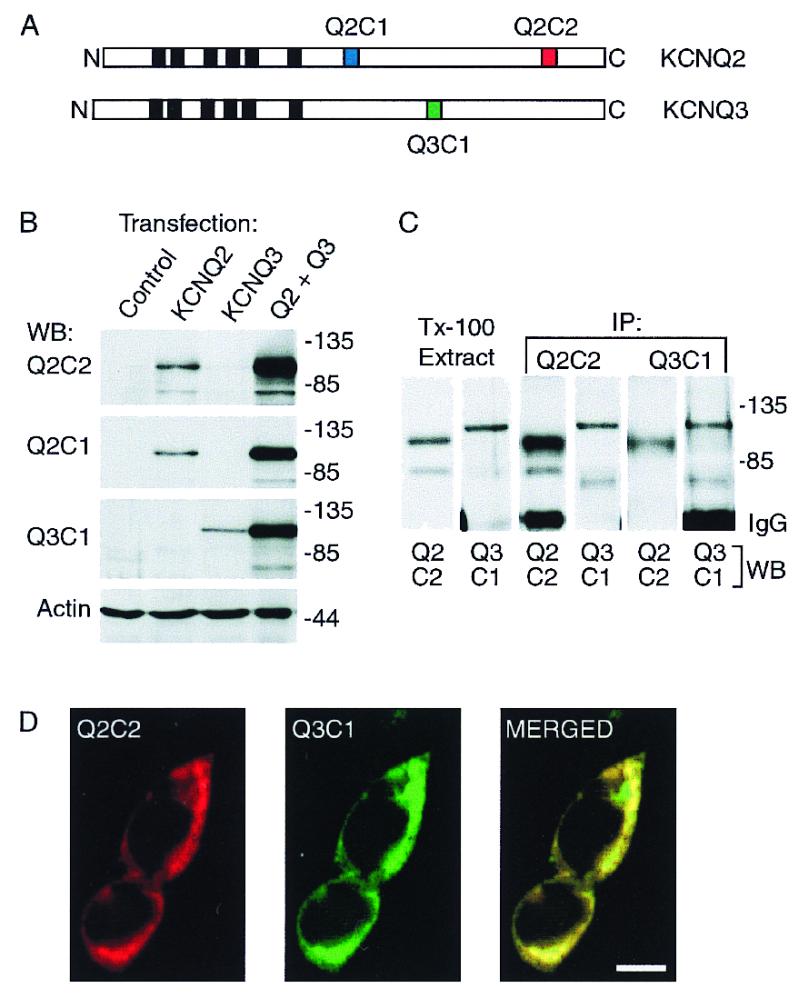
Characterization of heterologously expressed KCNQ2 and KCNQ3 and subunit-specific antibodies. (A) Diagram of the KCNQ2 and KCNQ3 polypeptides predicted by cDNA sequences, showing the position of the six putative membrane-spanning segments (black boxes), and the three segments within the C-terminal domains corresponding to synthetic peptides used for raising subunit-specific antibodies Q2C1, Q2C2, and Q3C1. (B) Immunoblots of whole-cell lysates prepared from HEK293 cells transfected with KCNQ2 alone, KCNQ3 alone, or cotransfected with both subunits. (C) Solubilization and coimmunoprecipitation of KCNQ2 and KCNQ3 expressed in HEK293 cells. Cells cotransfected with KCNQ2 and KCNQ3 were lysed under nondenaturing conditions with 1% Triton X-100. The lysates were cleared of nuclei and insoluble material by centrifugation, then either reserved (Tx-100 extract) or incubated with Q2C2 or Q3C1 antibodies. Whole-cell extracts and immunoprecipitates were probed with Q2C2, then stripped and reprobed with Q3C1. (D) Immunofluorescence staining of cotransfected HEK cells shows predominantly colocalized pattern of expression of KCNQ2 and KCNQ3. (Scale bar equals 10 μm.)
