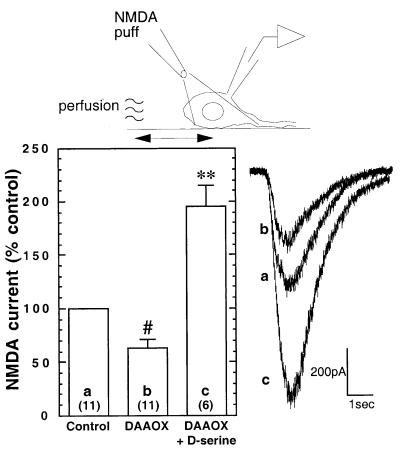
Figure 6.
DAAOX reduces NMDA receptor currents evoked with the micropuffer perfusion technique in cultured hippocampal neurons. To avoid washing away endogenous d-serine, NMDA (100 μM, 1 sec) was applied by gentle pressure ejection from a puffer pipette located ≈50 μm from the cell soma. Perfusion with DAAOX (1–10 μg/ml) attenuates the response to NMDA. The effect of DAAOX is fully reversed by the application of d-serine (100 μM), which also potentiates the NMDA-evoked current response. Recordings were in the presence of 1 μM tetrodotoxin. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM percent change in peak current amplitude with respect to control. Total number of recordings for each condition are shown in parentheses. Representative traces are shown to the right. Statistical significance was evaluated by using ANOVA analysis followed by Scheffé posthoc comparison. #, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.0001.