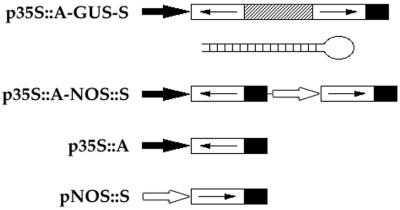
Figure 1.
Gene constructs used to analyze dsRNA effects. In p35S∷A-GUS-S, gene-specific sequences (open boxes with arrows indicating the orientation) in the antisense (A) and sense (S) orientations were linked with a 1,022-bp fragment of the GUS gene (hatched box) and controlled by the 35S promoter (solid arrow). A schematic structure of the predicted dsRNA stem with a single-stranded loop generated by p35S∷A-GUS-S constructs is shown. In p35S∷A-NOS∷S, gene-specific sequences in the antisense and sense orientations were controlled by the 35S promoter and the nopaline synthase promoter, respectively (open arrow). p35S∷A contains gene-specific sequences in the antisense orientation under control of the 35S promoter. pNOS∷S contains gene-specific sequences in the sense orientation driven by the nopaline synthase promoter. Solid box, the 3′ end of nopaline synthase.