Abstract
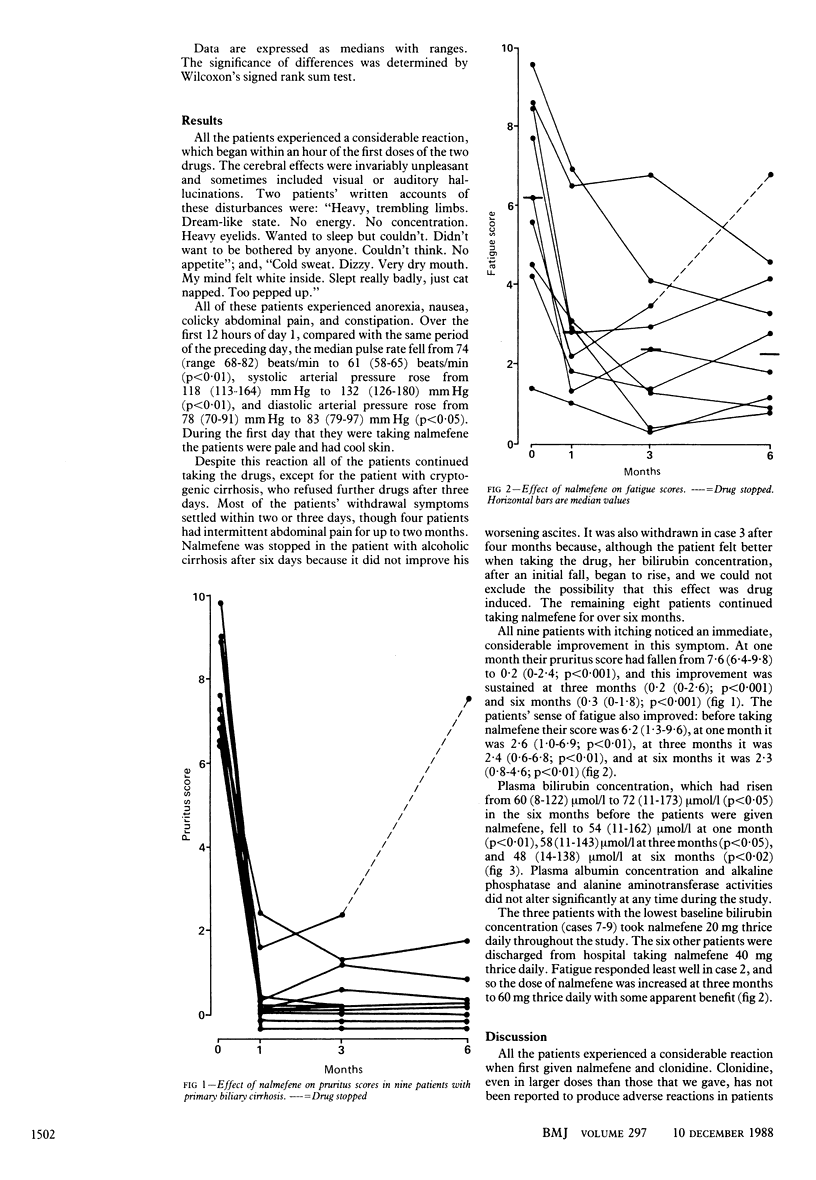
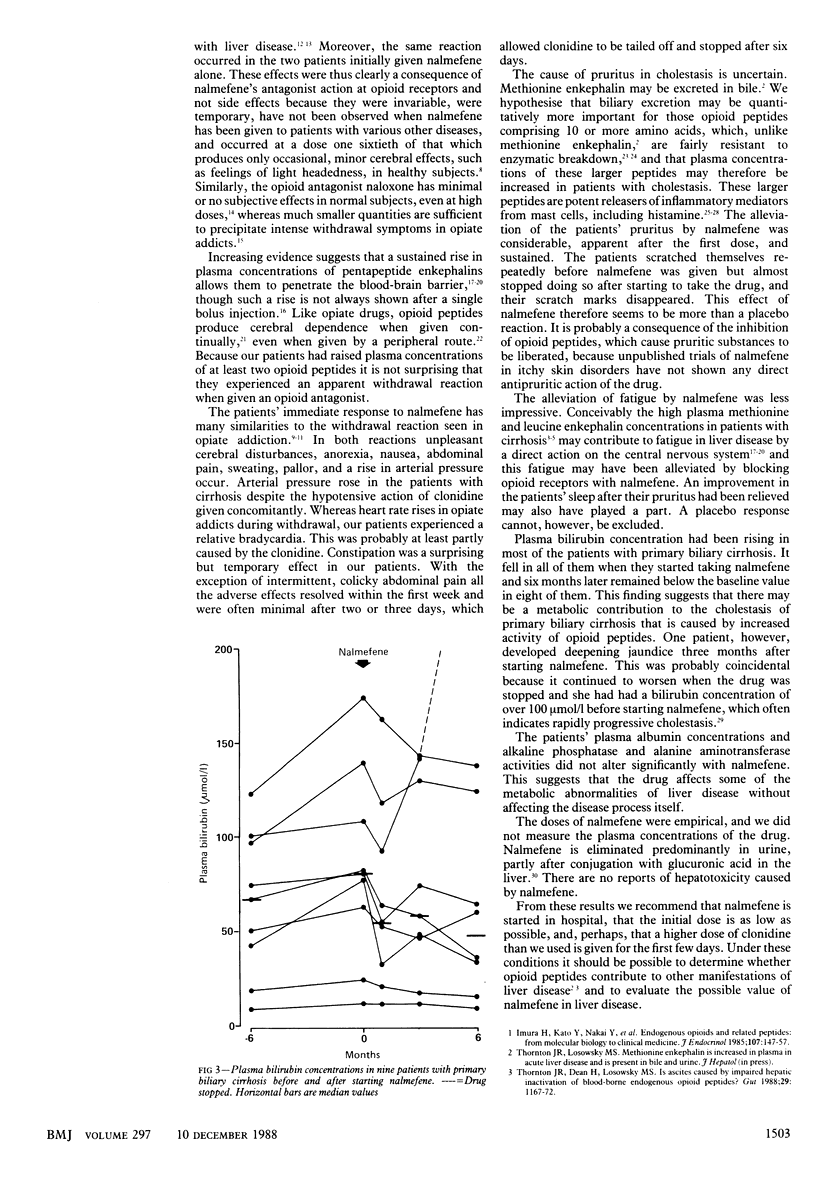
Patients with liver disease have increased plasma concentrations of the endogenous opioid peptides methionine enkephalin and leucine enkephalin. As an initial investigation to determine whether opioid peptides contribute to any of the clinical manifestations of hepatic disease nalmefene, a specific opioid antagonist devoid of agonist activity, was given to 11 patients with cirrhosis. They all experienced a severe opioid withdrawal reaction on starting the drug. In the nine patients with primary biliary cirrhosis pruritus was greatly alleviated, fatigue seemed to improve, and plasma bilirubin concentration, which had been rising, showed a modest fall in all except one patient. These results indicate that blocking opioid receptors has an effect on some of the metabolic abnormalities of liver disease.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banks W. A., Kastin A. J., Fischman A. J., Coy D. H., Strauss S. L. Carrier-mediated transport of enkephalins and N-Tyr-MIF-1 across blood-brain barrier. Am J Physiol. 1986 Oct;251(4 Pt 1):E477–E482. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.251.4.E477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casale T. B., Bowman S., Kaliner M. Induction of human cutaneous mast cell degranulation by opiates and endogenous opioid peptides: evidence for opiate and nonopiate receptor participation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984 Jun;73(6):775–781. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(84)90447-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charney D. S., Heninger G. R., Kleber H. D. The combined use of clonidine and naltrexone as a rapid, safe, and effective treatment of abrupt withdrawal from methadone. Am J Psychiatry. 1986 Jul;143(7):831–837. doi: 10.1176/ajp.143.7.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett A. D., Paterson S. J., McKnight A. T., Magnan J., Kosterlitz H. W. Dynorphin and dynorphin are ligands for the kappa-subtype of opiate receptor. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):79–81. doi: 10.1038/299079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornford E. M., Braun L. D., Crane P. D., Oldendorf W. H. Blood-brain barrier restriction of peptides and the low uptake of enkephalins. Endocrinology. 1978 Oct;103(4):1297–1303. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-4-1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R., Howes J., Gentile J., Hsu H. B., Hsiao J., Garg D., Weidler D., Meyer M., Tuttle R. Nalmefene: intravenous safety and kinetics of a new opioid antagonist. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1986 Jan;39(1):49–53. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1986.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gal T. J., DiFazio C. A., Dixon R. Prolonged blockade of opioid effect with oral nalmefene. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1986 Nov;40(5):537–542. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1986.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmerek D. E., Woods J. H. Kappa receptor mediated opioid dependence in rhesus monkeys. Life Sci. 1986 Sep 15;39(11):987–992. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90287-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. S., Redmond D. E., Jr, Kleber H. D. Clonidine blocks acute opiate-withdrawal symptoms. Lancet. 1978 Sep 16;2(8090):599–602. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92823-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A., Stubbs W. A., Gaillard R. C., Delitala G., Rees L. H., Besser G. M. Studies off the opiate control of prolactin, GH and TSH. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1981 Apr;14(4):381–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1981.tb00624.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh L. B. Reaction of opioid peptides with neutral endopeptidase ("enkephalinase"). J Neurochem. 1984 Aug;43(2):487–493. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb00925.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imura H., Kato Y., Nakai Y., Nakao K., Tanaka I., Jingami H., Koh T., Yoshimasa T., Tsukada T., Suda M. Endogenous opioids and related peptides: from molecular biology to clinical medicine. The Sir Henry Dale lecture for 1985. J Endocrinol. 1985 Nov;107(2):147–157. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1070147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastin A. J., Nissen C., Schally A. V., Coy D. H. Blood-brain barrier, half-time disappearance, and brain distribution for labeled enkephalin and a potent analog. Brain Res Bull. 1976 Nov-Dec;1(6):583–589. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(76)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. E., Bolger G., Weissman B. A. Binding of a new opiate antagonist, nalmefene, to rat brain membranes. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 1985 Apr;7(4):175–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau R., Lee S. S., Hadengue A., Braillon A., Lebrec D. Hemodynamic effects of a clonidine-induced decrease in sympathetic tone in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1987 Jan-Feb;7(1):149–154. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport S. I., Klee W. A., Pettigrew K. D., Ohno K. Entry of opioid peptides into the central nervous system. Science. 1980 Jan 4;207(4426):84–86. doi: 10.1126/science.7350645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick R. B., Kestenbaum R. S., Washton A., Poole D. Naloxone-precipitated withdrawal: a method for rapid induction onto naltrexone. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1977 Apr;21(4):409–413. doi: 10.1002/cpt1977214409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanahan F., Lee T. D., Bienenstock J., Befus A. D. The influence of endorphins on peritoneal and mucosal mast cell secretion. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984 Oct;74(4 Pt 1):499–504. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(84)90385-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J. M., Smith H., Schaffner F. Serum bilirubin: a prognostic factor in primary biliary cirrhosis. Gut. 1979 Feb;20(2):137–140. doi: 10.1136/gut.20.2.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton J. R., Dean H., Losowsky M. S. Is ascites caused by impaired hepatic inactivation of blood borne endogenous opioid peptides? Gut. 1988 Sep;29(9):1167–1172. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.9.1167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton J. R., Losowsky M. S. Plasma methionine enkephalin concentration and prognosis in primary biliary cirrhosis. BMJ. 1988 Nov 12;297(6658):1241–1242. doi: 10.1136/bmj.297.6658.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washton A. M., Resnick R. B. Clonidine for opiate detoxification: outpatient clinical trials. Am J Psychiatry. 1980 Sep;137(9):1121–1122. doi: 10.1176/ajp.137.9.1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei E., Loh H. Physical dependence of opiate-like peptides. Science. 1976 Sep 24;193(4259):1262–1263. doi: 10.1126/science.986687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willett I. R., Esler M., Jennings G., Dudley F. J. Sympathetic tone modulates portal venous pressure in alcoholic cirrhosis. Lancet. 1986 Oct 25;2(8513):939–943. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90599-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki Y., Shimamura O., Kizu A., Nakagawa M., Ijichi H. IgE-mediated 14C-serotonin release from rat mast cells modulated by morphine and endorphins. Life Sci. 1982 Aug 2;31(5):471–478. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90333-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zloković B. V., Lipovac M. N., Begley D. J., Davson H., Rakić L. Transport of leucine-enkephalin across the blood-brain barrier in the perfused guinea pig brain. J Neurochem. 1987 Jul;49(1):310–315. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb03431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


