Figure 1.
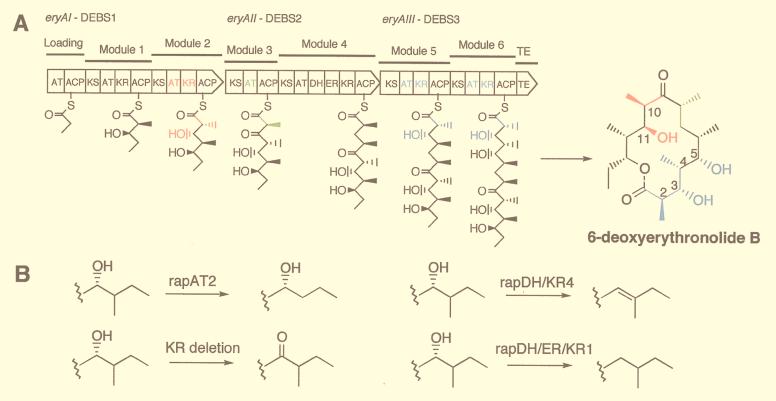
Wild-type and mutant forms of the eryA genes and DEBS proteins. (A) The eryAI–eryAIII genes and proteins are shown as broad arrows oriented in the direction of transcription with the domains in modules 1 to 6 of DEBS1-DEBS3, indicated by the symbols explained in the text. The first substrate, propionyl-CoA, is attached to the loading domain ACP and (2S)-2-methylmalonyl-CoA to the module 2 ACP. Then, a decarboxylative condensation between the propionate and methylmalonate takes place followed by reduction of the incipient β-ketone to form the intermediate shown attached to the ACP of module 2. This intermediate is transferred to the ACP of module 3, and the sequence of reactions is repeated at each of the other modules with or without ketone reduction, dehydration, or double bond reduction to form the linear 21-carbon polyketide attached to the ACP of module 6, which then is cyclized and released as 6dEB. (B) Replacement of the one or more of the colored domains in DEBS1, DEBS2, or DEBS3 with one of the three rap PKS domains or cassettes, or deletion of the KR, results in the corresponding functional group changes shown at one or more of the colored positions of 6dEB.