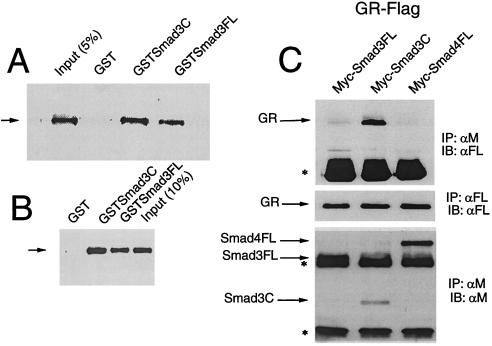
Figure 4.
Smad3 activation domain interacts with GR in vitro and in vivo. (A) GST pull-down assays were carried out by incubating whole cell extracts prepared from COS cells expressing functional Flag-tag GR with GST-Smad fusion proteins, including the C-terminal activation domain of Smad 3 (amino acids 172–425, GST-Smad3C) or full-length Smad3 (GST-Smad3 FL), immobilized on glutathione-agarose beads. Bound proteins were identified by immunoblotting Flag-GR, by using anti-Flag M2 monoclonal antibody and chemiluminescence. (B) Similar studies were performed by using in vitro-translated GR-Flag. In vitro transcription and translation reactions were carried out by using the TNT-coupled reticulocyte lysate system (Promega). (C) Coimmunoprecipitation analysis. COS cells were transfected with pCMVGR-Flag and Myc-tagged Smads, as indicated, by using lipofectamine, and cultured in the presence of 100 nM Dex for 48 h. Cell extracts were incubated with anti-Myc or anti-Flag antibody and protein A-Sepharose. GR/Smad complexes were detected by immunoprecipitation with anti-Myc 9E10 monoclonal antibodies and immunoblotting by using anti-Flag M2 antibodies and chemiluminescence. The arrow indicates the position of GR and the asterisk, the position of immunoglobulins. IP: immunoprecipitation; IB: immunoblotting. Middle shows the expression of GR-Flag; Bottom shows the expression of the Myc-tagged Smads.