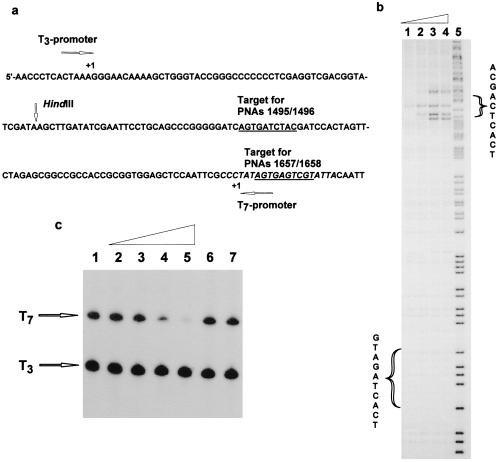
Figure 3.
Binding of anti-T7-promoter PNAs 1657/1658 (H-Lys-DCGDCsUCDCsU-Lys-NH2/H-Lys-DGsUGDGsUCGsU-Lys-NH2) to their target and effect on T7-transciption. (a) Sequence showing the T7 promoter and the PNA targets. (b) KMnO4 probing of the binding of PNAs 1657/1658 to their target. The experiment was performed as described for Fig. 2c. The PNA concentrations in lanes 1–4 were 30 nM, 90 nM, 3 mM, and 9 mM. Lane 5 is an A/G sequence marker. (c) Effect on T7 transcription of the binding of promoter-directed PNAs 1657/1658. The PNAs were prebound to the DNA (p206 cut with HindIII) for 16 hr at 37°C in 10 mM Tris⋅HCl/1 mM EDTA buffer, pH 7.4. Subsequently polymerase buffer, NTP mix containing [32P]UTP and T7 and T3 RNA polymerases were added and transcription was allowed to proceed for 1 min at 37°C. The transcripts were analyzed by PAGE and autoradiography. The following concentrations (mM,) of PNAs were used (PNA 1657/PNA 1658): lane 1, 0/0; lane 2, 0.03/0.03; lane 3, 0.1/0.1; lane 4, 0.3/0.3; lane 5, 1/1; lane 6, 0.3/0; lane 7, 0/0.3. As an internal control, transcription with RNA polymerase T3, for which the promoter does not contain the PNA-binding site, was performed simultaneously.