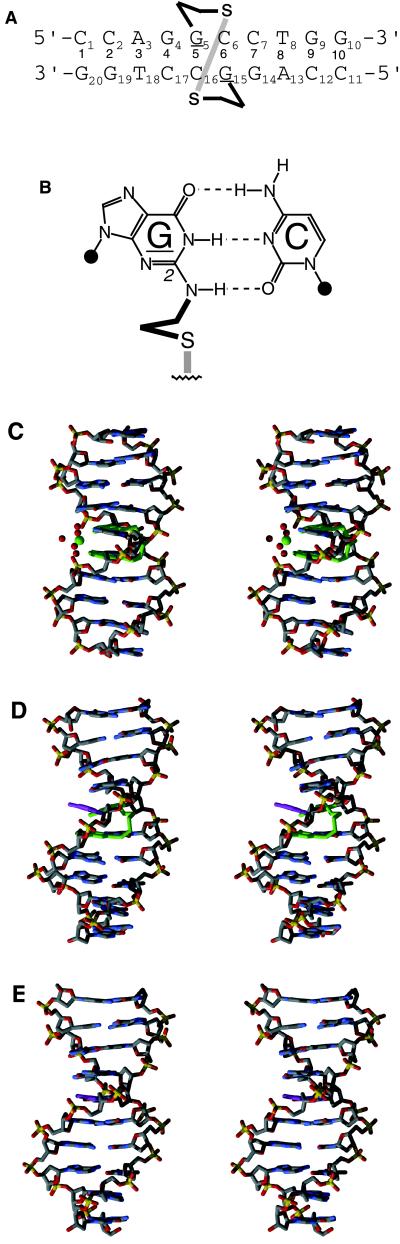
Figure 1.
(A) Sequence of the C2-crosslinked DNA decamer used in this study. The underlined G nucleotides denote the crosslinked guanines. (B) Chemical structure of a base pair containing the tether on the amino group in the minor groove of guanine. Stereo images of duplex A (C) and duplex B (D). The crosslinked guanines and the crosslink bridges are colored green. In duplex A, the calcium ion (green) and its liganding water molecules (red) are shown. In duplex B, the partially flipped-out cytosine (C6) is shown in magenta. (E) A canonical B–DNA duplex shown in the same orientation as duplex B with the cytosine corresponding to the partially flipped-out one, C6 in duplex B, shown in magenta for reference. By comparison, it is clear how much C6 is swung out and into the major groove. Fig. 1 C–E as well as Figs. 3 and 4 were prepared with the programs bobscript (38), molscript (39), and raster 3d (40, 41).