Figure 2.
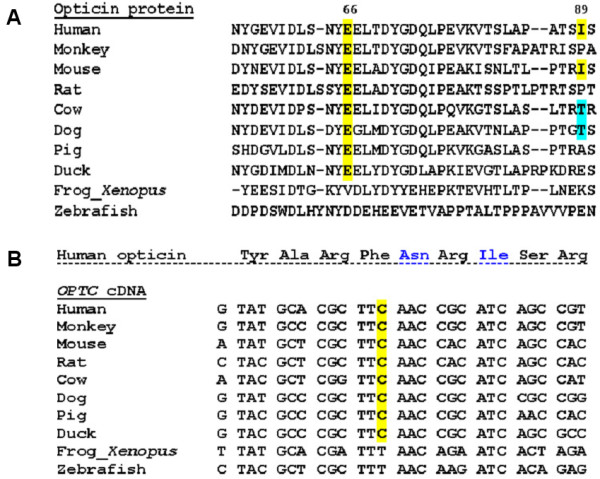
Evolutionary conservation status of the silent change at cDNA level and other two nucleotide variants at protein level found in OPTC. (A): Multiple sequence alignment of opticin protein showing the conservation status of p.Glu66 (c.313A>G) residue and p.Ile89 (c.382T>C) residue across different vertebrate species. The sources of the sequences are NCBI: NP_055174.1 (human), XP_001102193.1 (monkey), NP_473417.1 (mouse), XP_222641.4 (rat), NP_991339.1 (cow), NP_001003056.1 (dog), NP_999173.1 (pig), NP_989804.1 (duck), NP_001016499.1 (Xenopus), ABB53599.1 (zebrafish). Except two lower vertebrates (Xenopus and zebrafish), p.66 (c.313A>G) is conserved in all higher vertebrate species, while p.Ile89 (c.382T>C) is conserved only in human and mouse. In both cases, multiple sequence alignment was done using ClustalW of EMBL-EBI [39] (B): Multiple sequence alignment of OPTC cDNA shows conservation of the wobble base for p.Phe162 which is altered (C>T) in case of a POAG patient (GL42 in Table 1). The sources of the sequences are GenBank: NM_014359 (human), XM_001102193.1 (monkey), NM_054076.1 (mouse), XM_001061460.1 (rat), NM_205770.1 (cow), NM_001003056.1 (dog), NM_214008.1 (pig), NM_204473.1 (duck), NM_001016499.2 (Xenopus) and NM_001003583.1 (zebrafish). Also, corresponding amino acid sequence of human opticin (NP_055174.1) is given above; except two lower vertebrates (Xenopus and zebrafish), c.602C (p.Phe162) is conserved in all higher vertebrate species.
