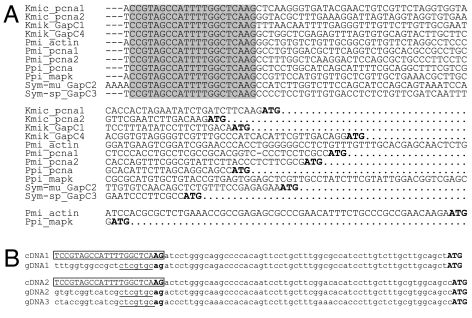
Fig. 1.
The conserved SL sequence from dinoflagellate mRNAs. (A) Alignment of the 5′ end of several full-length dinoflagellate cDNAs. The 21-nt identical sequence is shaded. ATG in bold indicates the predicted start codon. Kmic, K. micrum; Kmik, Kar. mikimotoi; Pmi, Pr. minimum; Ppi, P. piscicida; Sym-mu, S. muscatinei; Sym-sp, Symbiodinium sp. (B) Alignment of the 5′ UTRs of P. piscicida pcna cDNAs and corresponding genomic (gDNA) clones revealing the 22-nt trans-spliced SL (boxed). cDNA1, GenBank accession no. DQ239852; gDNA1, DQ239839; cDNA2, DQ239853; gDNA2, DQ239842; gDNA3, DQ239843. The dinucleotide AG at the SL-mRNA boundary is in bold. Underlined are the 5′ end conserved sequence in different genomic clones, ended with the 3′ acceptor splice site AG.