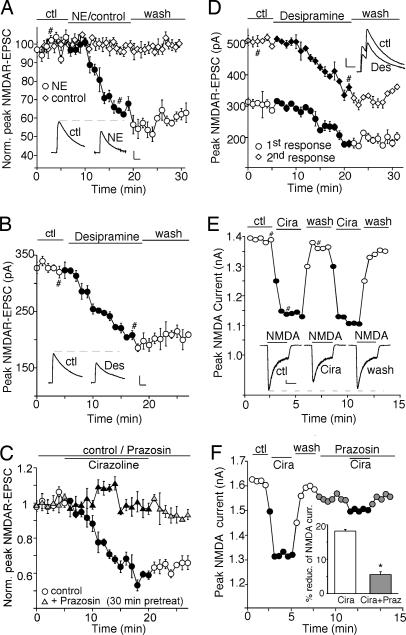
Fig. 1.
Activation of α1-ARs reduces the amplitude of NMDAR-EPSC and whole-cell NMDAR currents. (A–C) Plot of peak NMDAR-EPSC in PFC slices showing the effect of 100 μM norepinephrine (A), 20 μM norepinephrine transporter inhibitor desipramine (B), or 40 μM α1-AR agonist cirazoline in the absence or presence of 40 μM α1-AR antagonist prazosin (C). (D) Plot of peak NMDAR-EPSC evoked by double pulses (interstimuli interval, 100 ms) as a function of time and 20 μM desipramine application. (Insets A, B, and D) Representative current traces (average of three trials) at time points denoted by #. (Scale bars: 100 pA, 0.1 s.) (E and F) Plot of peak 100 μM NMDA-evoked currents in dissociated PFC pyramidal neurons showing the effect of 40 μM cirazoline (E) and its blockade by 40 μM prazosin (F). (Inset E) Representative current traces (at time points denoted by #). (Scale bars: 100 pA, 1 s.) (Inset F) Cumulative data (mean ± SEM) summarizing the percentage reduction of NMDAR currents by cirazoline in the absence or presence of prazosin. ∗, P < 0.01, ANOVA.