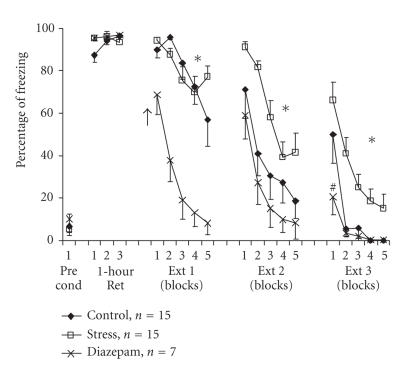
Figure 3.
Diazepam overcomes stress-induced impairment of the extinction of auditory fear. Rats were exposed to 3 pairings of a tone with a mild foot shock in the conditioning chamber. On the next day, control animals remained in their home cages, “diazepam” group animals were injected with diazepam (2 mg/kg, IP) 20 minutes before being placed on an elevated platform for 30 minutes, while “stress” group animals were placed directly onto the elevated platform for 30 minutes, without prior administration of the drug. Immediately afterwards, animals were taken for extinction training and were exposed to15 tones (Ext 1) with no shock. Animals were exposed to an additional 15 tones on days 3 (Ext 2) and 4 (Ext 3) with no drug or shock. There were significant differences between the diazepam group and the other groups during Ext 1 (P < .001). On Ext 2 and Ext 3, the stress group was significantly different from the control (Ext 2: P < .05, Ext 3: P < .01) and the diazepam (Ext 2: P < .01, Ext 3: P < .001) groups. Arrow denotes time of drug infusion. The Pre cond data points indicate the amount of freezing exhibited by rats prior to commencement of fear conditioning.