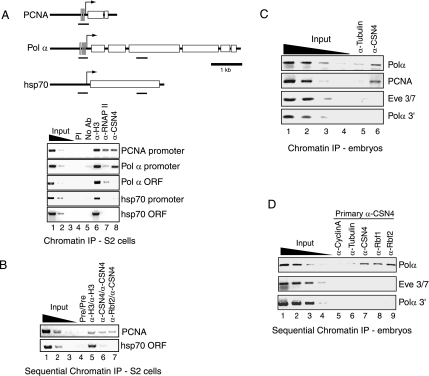
Figure 4.
CSN4 co-occupies target gene promoters with Rbf1 and Rbf2. (A) CSN4 associates with Rbf target genes in Drosophila S2 cells. Formaldehyde cross-linked chromatin was prepared from Drosophila S2 cells and immunoprecipitated using the indicated antibodies in single-round reactions. Enrichment of the Rbf-regulated Polα and PCNA promoters was observed by α-CSN4 immunoprecipitation reactions (lane 8), but not in reactions lacking antibody (lane 4) or using preimmune serum (PI, lane 5). Lanes 1–3 show the amplification signals for 1, 0.1, and 0.01% of the input chromatin. A schematic of the genes examined is shown at the top with the positions of E2F-binding sites indicated by gray vertical bars. The various regions amplified by PCR are indicated by the small black horizontal bars. (B) Rbf2 and CSN4 co-occupy the PCNA promoter in Drosophila S2 cells. Sequential chromatin immunoprecipitation of S2 cell chromatin was performed with preimmune serum (lane 4), α-histone H3 (lane 5), α-CSN4 (lane 6), or α-Rbf2 antibodies (lane 7). Chromatin was recovered by elution with DTT and SDS followed by dilution for the second-round immunoprecipitation using the indicated antibodies. (C) CSN4 associates with Rbf target genes in Drosophila embryos. Formaldehyde cross-linked chromatin was prepared from 0- to 12-h-old wild-type Drosophila embryos for immunoprecipitation using α-tubulin (lane 5) or α-CSN4 antibodies (lane 6). Lanes 1–4 show the amplification signal for 10, 1, 0.1, and 0.01% of the input chromatin. (D) CSN4 simultaneously occupies the Polα promoter along with Rbf1 and Rbf2 in Drosophila embryos. Primary immunoprecipitation using formaldehyde cross-linked chromatin from 0- to 12-h-old embryos was carried out first with α-CSN4 antibody followed by a second immunoprecipitation with the indicated antibodies. Enrichment of the Polα but not the eve stripe 3/7 enhancer or Polα 3′ region was observed in the second-round Rbf1 and Rbf2 immunoprecipitation reactions.