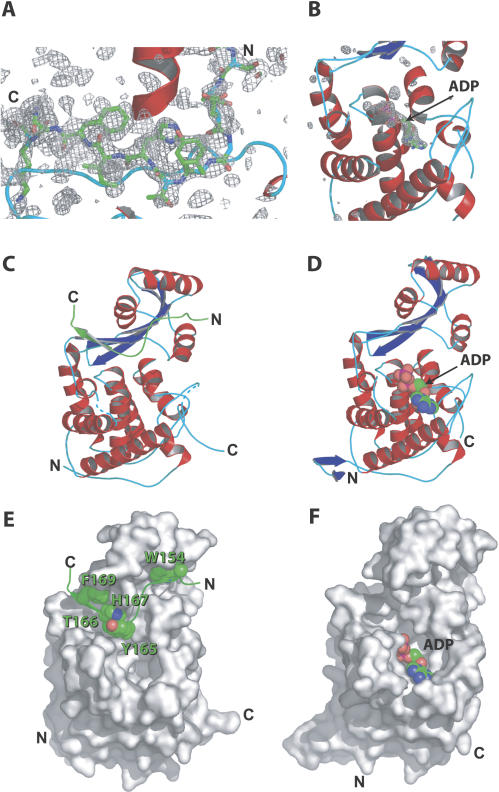
Figure 1. Structures of AvrB Complexed with RIN4142–176 and ADP.
(A) Difference electron density (F o − F c) from AvrB/RIN4142–176 crystals centered on the C-terminal β-strand of RIN4142–176 (green sticks) following molecular replacement with two AvrB molecules (PDB 1NH1).
(B) Difference electron density (F o − F c) from AvrB crystals soaked with ADP following molecular replacement with 1 AvrB (PDB 1NH1).
For (A) and (B), densities are contoured at 2 and 4 σ, respectively.
(C and D) Ribbon diagrams of the AvrB/RIN4142–176 and AvrB/ADP complexes, respectively. AvrB helices, strands, and loops are red, blue, and cyan, respectively, and the RIN4142–176 ribbon is green. The overall structures are similar, and the different AvrB N and C termini between them likely reflects differences in their packing interfaces.
(E and F) Surface representations of AvrB in the AvrB/RIN4142–176 and AvrB/ADP complexes, respectively. (E) RIN4142–176 is shown as a ribbon diagram with the side-chains of W154, Y165, T166, H167, and F169 represented as spheres to emphasize the surface grooves and concavities in AvrB that buries these residues. Note that the views represented in (C) and (E) and in (D) and (F) are identical.