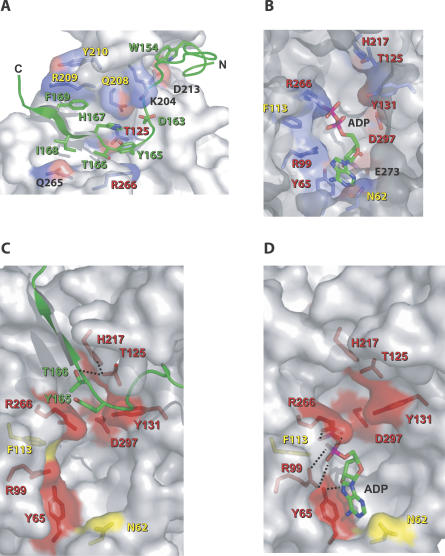
Figure 2. Close-Up Views of the AvrB/RIN4142–176 and AvrB/ADP Interfaces.
(A and B) A semitransparent representation of the AvrB surface showing selected AvrB side-chains that contact RIN4142–176 [green in (A)] and ADP in (B). Atoms of ADP and RIN4142–176 side-chains are colored by type: C (green), N (blue), O (red), and P (pink). AvrB side-chains are coded by atom type; C (light blue), N (blue), and O (red). Positive and negative surface charges of the indicated AvrB side-chains are color coded blue and red, respectively. Text for AvrB residues that were mutated and tested for their ability to trigger RPM1 function are color coded as follows: red, full loss of function; yellow, partial loss of function; black, no loss of function.
(C and D) A close-in semitransparent representation of the AvrB surface highlighting the functional requirement (complete, red; partial, yellow) for AvrB amino acids in triggering RPM1 function. Relevant side-chains and surfaces of AvrB residues are displayed as stick representations with color-coded labels as in (A) and (B). Stick representations of residues from RIN4142–176 are labeled green in (C), and a stick representation of ADP is highlighted in (D).