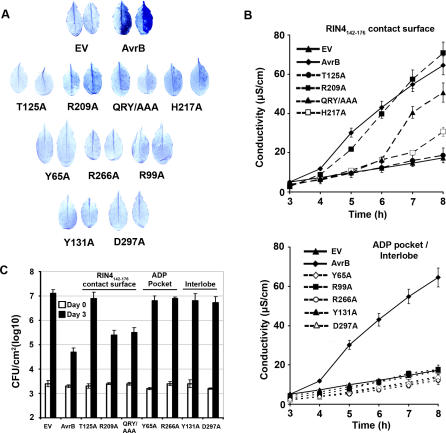
Figure 4. Interactions with RIN4 and ADP Are Required for AvrB Function in Activating RPM1.
(A) Trypan blue staining of Arabidopsis Col-0 (RPM1) leaves 5 h after infection with Pto DC3000 expressing wild-type or mutant versions of HA-epitope tagged AvrB. EV is an empty vector (pBBR1 MCS-2) used as a negative control in Pto DC3000. QRY/AAA is a triple mutation of AvrB Q208, R209, and Y210 to alanine. Trypan blue staining of five infected leaves per construct was repeated twice in two independent experiments, and two representative leaves per AvrB mutant are presented.
(B) Quantification of HR by electrolyte leakage (mean ± 2 SE) from leaves infected with Pto DC3000 expressing AvrB and mutant derivatives as labeled. The experiment was performed as in (A) and was repeated twice with similar results. Solid black lines represent the negative Pto DC3000(EV) (black triangles) and positive controls Pto DC3000(avrB-HA) (black diamonds). In the top graph, hatched lines represent mutations of AvrB residues making contacts with RIN4142–176 from the crystal structure presented in Figure 2. In the bottom graph, dotted lines represent mutations of AvrB residues lining the ADP binding pocket, from the crystal structure presented in Figure 2.
(C) Growth of Pto DC3000 expressing the wild-type or selected alanine mutant versions AvrB-HA on Arabidopsis Col-0(RPM1). White and black bars represent the bacterial populations at the time of inoculation (day 0) and 3 d postinoculation (day 3), respectively. Bars indicate the mean of four samples ± 2 SE and are representative of two independent experiments.