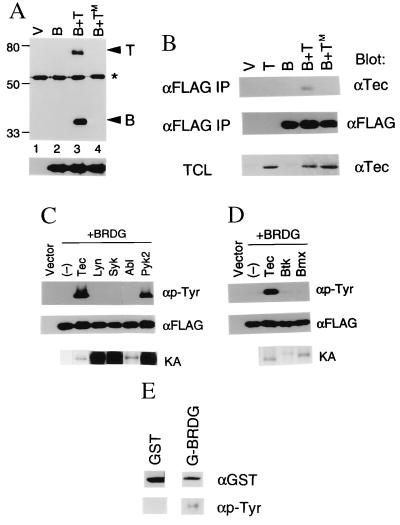
Figure 2.
(A) Tec-induced phosphorylation of BRDG1 in vivo. Ten micrograms of pcDNA3-FLAG vector (V) or of pcDNA-BRDG-F (B) were introduced into 293 cells (2 × 106) by the calcium phosphate method either alone or together with expression plasmids encoding either Tec (T) or a kinase-defective mutant of Tec (TM). After 48 h of culture, cells were lysed and BRDG1 was immunoprecipitated with antibodies to FLAG. The resulting precipitates were fractionated by SDS/PAGE on a 7.5% gel and subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies to either phosphotyrosine or FLAG. The positions of Tec and BRDG1 are indicated at the bottom, and positions of molecular size standards (in kilodaltons) are on the left. The asterisk denotes the position of IgH. (B) Physical interaction of BRDG1 with Tec in intact 293 cells. Cells transfected with the empty vector (V) or with vectors encoding BRDG1 (B), Tec (T), or TecKM (TM) as indicated at the top were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with antibodies to FLAG (αFLAG), and the resulting precipitates were then subjected to immunoblot analysis either with antibodies to Tec (αTec) or FLAG. Total cell lysates (TCL) (10 μg of protein) of each set were also subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-Tec antibody. (C) Effects of various PTKs on phosphorylation of BRDG1 in 293 cells. Cells were transfected with empty vector (Vector) or with pcDNA-BRDG-F (+BRDG) in the absence (−) or presence of expression plasmids encoding Tec, Lyn, Syk, c-Abl, or Pyk2. BRDG1 was immunoprecipitated from the various transfected cells with anti-FLAG antibody and then subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies to phosphotyrosine (αp-Tyr) or to FLAG (αFLAG). The PTKs were also immunoprecipitated from the same set of cells and subjected to an in vitro kinase assay without exogenous substrates. Autophosphorylation of each PTK (KA) is shown at the bottom. (D) Effects of various Tec family kinases on BRDG1 phosphorylation in 293 cells. Cells were transfected with empty vector (Vector) or with pcDNA-BRDG-F (+BRDG) in the absence (−) or presence of expression plasmids encoding Tec, Btk, or Bmx. BRDG1 was immunoprecipitated from the transfected cells and probed with antibodies to phosphotyrosine or FLAG. Autophosphorylation activity of each PTK (KA) is shown at the bottom. (E) Phosphorylation of BRDG1 by Tec in vitro. Immunoprecipitates prepared from 293 cells expressing Tec with anti-Tec antibody were washed and then incubated at 37°C for 15 min with 0.1 mM ATP plus 1 μg of GST or GST-BRDG1 (G-BRDG), as indicated at the top. The samples were then subjected to the immunoblot analysis with antibodies to GST (αGST) or to phosphotyrosine (αp-Tyr).