Fig. 5.
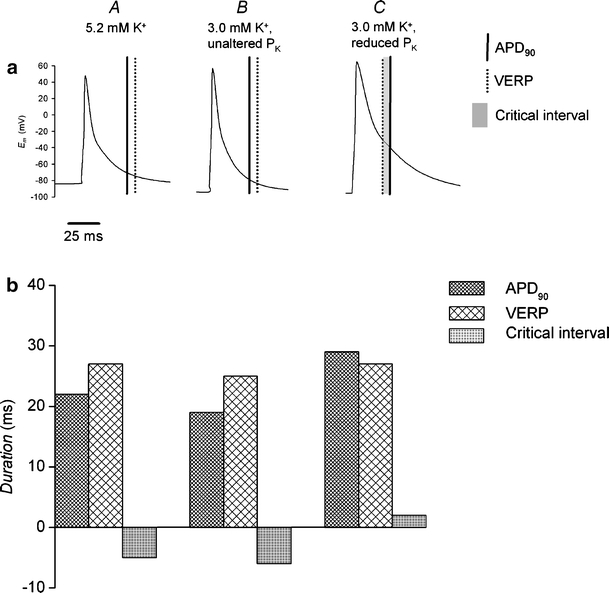
Computational modeling of murine ventricular action potentials showing changes in action potential duration, ventricular effective refractory period, and critical interval after exposure to hypokalemia. Action potential morphologies during regular stimulation in cells under normokalemic (5.2 mM K+, A) and hypokalemic (3.0 mM K+) conditions comparing action potential duration at 90% repolarization; APD90 (vertical solid lines), VERP (vertical broken lines), and critical interval (shading; a). In B, permeabilities of ion channel are under normokalemic conditions. In C, permeabilities of ion channels carrying the repolarizing K+ currents IK1 and Ito are reduced by 20%. APD90 (dense hashing), VERP (sparse hashing), and critical interval (shading) under these conditions (b)
