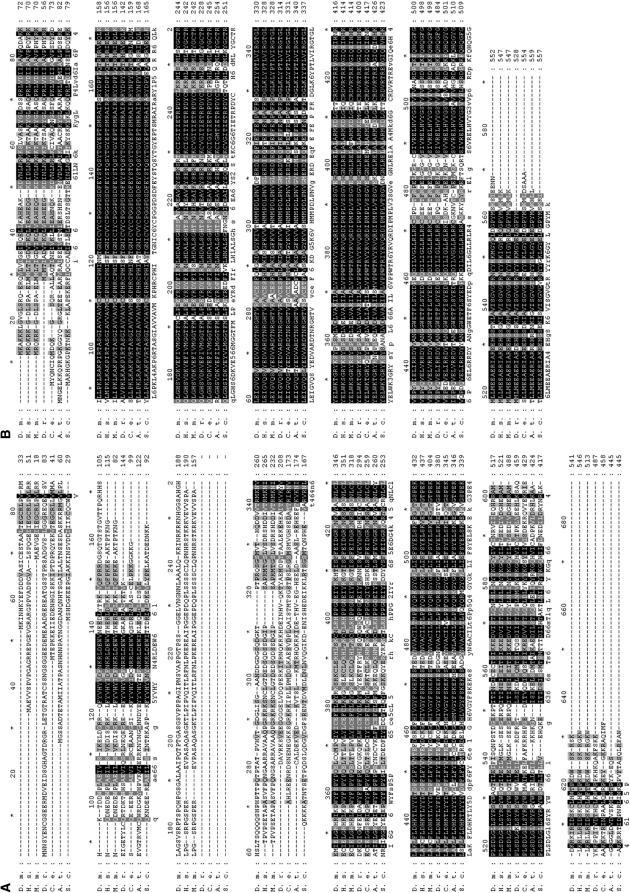
Figure 2.—
Dmel\Tip60 and Dmel\Elp3 are evolutionarily conserved among different species. Shown are the predicted amino acid sequences for the proteins encoded by (A) Dmel\Tip60 and (B) Dmel\Elp3 and their alignment with sequences encoded by ORFs from Homo sapiens (H.s.), M. musculus (M.m.), D. rerio (D.r.), C. elegans (C.e.), A. thaliana (A.t.), and S. cerevisiae (S.c.). Interspecies homology ranges from 29 to 56% identity (D.r. to M.m.)/41 to 68% similarity (D.r. to M.m.) for Dmel\Tip60 and 70–82% identity (A.t. to H.s.)/82–92% (A.t. to H.s.) similarity for Dmel\Elp3 over their entire coding region. Solid boxes and shaded backgrounds represent identical and similar amino acids, respectively. Alignment was carried out by Genedoc.