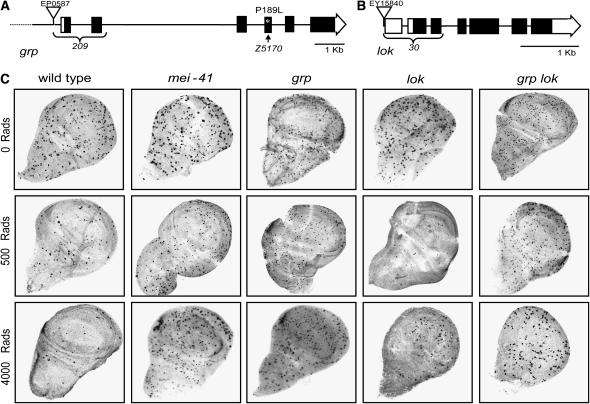
Figure 5.—
Checkpoint defects in grp and lok mutants. (A) Schematic of the genomic architecture of grp is shown. Each box represents an exon; solid regions designate protein-coding regions (the four alternative first exons, which are noncoding, are not shown). grp209 was generated by excision of EP587 (triangle) to generate a deletion that removes the first two coding exons (brace). grpZ5170 has a C-to-T transition that changes a conserved proline at residue 189 in the kinase domain to leucine (asterisk; see materials and methods for details). (B) The lok30 allele was generated by excision of EY15840 (triangle), generating a deletion of the 5′-UTR and the first two coding exons (brace). (C) DNA damage checkpoint defects in mutants. Third instar larvae of the indicated genotype were unirradiated (top) or irradiated with either 500 rad (middle) or 4000 rad (bottom) of γ-rays. Imaginal discs were dissected and fixed 1 hr after irradiation. Mitotic cells are revealed by staining with an antibody to phosphorylated histone H3.