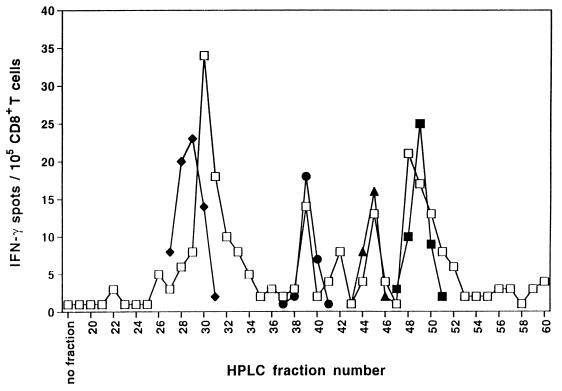
Figure 3.
HPLC-fractionated naturally processed peptides that have been acid-eluted from viable LCL cells contain multiple epitopes recognized by freshly isolated “memory” CD8+ T cells. Natural peptides were acid-eluted from 4 × 108 LCL cells derived from donor IP1 and separated by RP-HPLC. In parallel, synthetic latent EBV peptide antigens (4 μg each) known to be recognized by donor IP1’s CD8+ lymphocytes were also HPLC-fractionated using the identical protocol. Individual HPLC fractions of natural EBV peptides (10 μl ≈ 108 LCL cell equivalents per well) or synthetic EBV peptides [10 μl per well; EBNA-3A 379–387 (♦), EBNA-2 67–76 (●), LMP-2A 426–434 (▴), LMP-2 329–337 (■)] were tested for recognition by purified CD8+ T cells freshly isolated from the blood of donor IP1 in IFN-γ ELISPOT assay. Autologous immature DC were used as APC. Spots were developed after a culture period of 40 h and were evaluated as described in Fig. 1. Each value represents the mean spot number of duplicate determinations with 105 CD8+ T lymphocytes initially seeded per well. Results were confirmed in two independent experiments.