Figure 1.
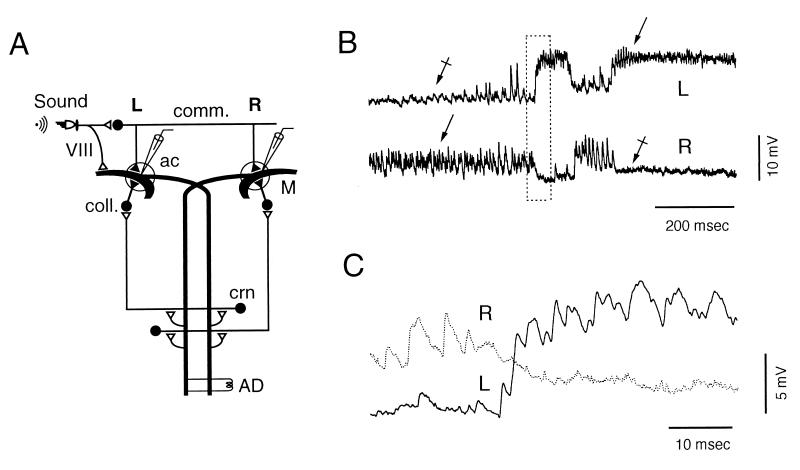
Alternate states of ISN. (A) Diagram of the experimental set-up and of M cells’ inhibitory networks. Action potentials were induced in the left (L) or the right (R) M cells by antidromic (AD) stimulation of the M axon(s) or by brief, intracellular current injections (≈1 msec) through the recording microelectrode. Both procedures activated the M cell ipsilateral recurrent pathway via the cranial relay neurons (crn), which synapse on collateral inhibitory interneurons (coll.). The commissural inhibitory interneurons (comm.), which terminate on both M cells, were activated by auditory stimuli via VIII nerve primary fibers. ac, axon cap. (▴ and ▵) Inhibitory and excitatory synapses, respectively. (B) Simultaneous intracellular recordings from both M cells. Bursts of fast IPSPs (arrows), present during the noisy state, disappear during the subsequent quiet period (crossed arrows). (C) Boxed region in B displayed at higher magnification and faster sweep speed.